CISOPlatform Breach Intelligence July 27, 2025 – Major Insurance & Dating App Breaches
Report Date: July 27, 2025 Coverage Period: July 26, 2025 Classification: Executive Intelligence BriefExecutive Summary
July 26, 2025 witnessed significant cybersecurity incidents affecting critical sectors including insurance and consumer applications. The most notable breach involved Allianz Life Insurance, where threat actors compromised a third-party CRM system through social engineering, affecting the majority of their 1.4 million customers. Concurrently, the Tea dating app disclosed a breach exposing 72,000 user images, including sensitive verification selfies. These incidents, combined with ongoing exploitation of Microsoft SharePoint vulnerabilities by China-linked APT groups, underscore the persistent threat landscape targeting both enterprise infrastructure and consumer privacy. The insurance sector continues to face targeted attacks, with security researchers attributing multiple recent breaches to the Scattered Spider collective.
Key Breach Incidents Overview
- Allianz Life Insurance Breach - Social engineering attack on third-party CRM system compromised PII of majority of 1.4M customers
- Tea Dating App Incident - 72,000 user images stolen including 13,000 verification selfies from gender verification process
- Microsoft SharePoint Zero-Day Exploitation - China-linked APT groups exploited incomplete patches affecting nearly 100 organizations globally
- FIDO Authentication Research - Expel retracted claims about PoisonSeed bypass technique after verification showed MFA challenges failed
- Insurance Sector Targeting - Continued wave of attacks attributed to Scattered Spider collective across multiple insurance providers
- Third-Party Risk Materialization - Multiple incidents highlighting vulnerabilities in cloud-based CRM and collaboration platforms
- State-Sponsored Activity - Persistent exploitation by APT27 (Linen Typhoon) and APT31 (Violet Typhoon) targeting collaboration platforms
Major Incident Analysis
1. Allianz Life Insurance Data Breach
Incident Timeline: July 16, 2025 (disclosed July 26) Attack Vector: Social engineering targeting third-party cloud-based CRM system Impact: Majority of 1.4 million customers, financial professionals, and select employees Attribution: Potentially linked to Scattered Spider collective based on attack patterns Technical Analysis: The Allianz Life breach represents a sophisticated social engineering attack targeting third-party infrastructure. Threat actors successfully compromised a cloud-based customer relationship management system, demonstrating the evolving threat landscape where attackers focus on supply chain vulnerabilities rather than direct organizational targets. Strategic Implications:- Third-party risk management failures in critical financial services
- Social engineering remains highly effective against cloud service providers
- Insurance sector faces coordinated targeting by advanced threat actors
- Regulatory compliance implications under state data protection laws
2. Tea Dating App Privacy Breach
Incident Timeline: July 26, 2025 Attack Vector: Unauthorized access to data storage systems Impact: 72,000 user images (13,000 verification selfies, 59,000 social images) Data Types: Biometric verification images, user-generated content, personal photos Technical Analysis: The Tea dating app breach highlights critical vulnerabilities in biometric data protection within consumer applications. The compromise of verification selfies presents significant identity theft and deepfake creation risks, while the broader image dataset enables sophisticated social engineering attacks. Privacy Implications:
- Biometric data exposure creates long-term identity risks
- Potential for AI-driven deepfake creation using stolen selfies
- Consumer trust erosion in dating platform security measures
- Regulatory scrutiny under emerging biometric privacy legislation
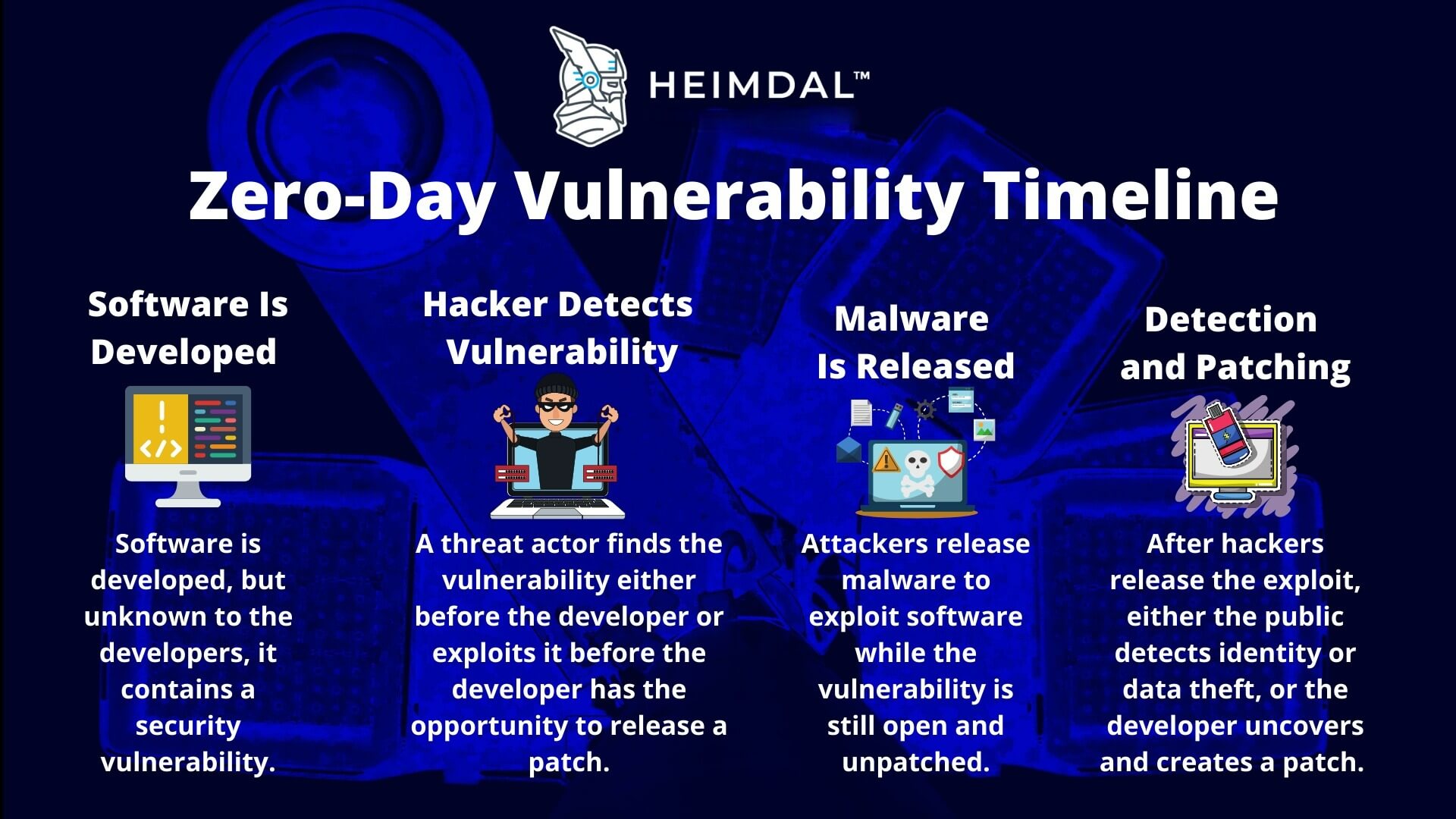
3. Microsoft SharePoint Zero-Day Campaign
Incident Timeline: July 18-26, 2025 (ongoing exploitation) Attack Vector: Zero-day exploitation of incomplete Microsoft patches Impact: Nearly 100 organizations globally across critical sectors Attribution: APT27 (Linen Typhoon), APT31 (Violet Typhoon), Storm-2603 CVE References: CVE-2025-53770, CVE-2025-53771 Technical Analysis: The SharePoint zero-day campaign demonstrates sophisticated state-sponsored capabilities in rapid exploit development. China-linked APT groups successfully reverse-engineered Microsoft's incomplete July 8 patch within hours, developing the "ToolShell" exploit for remote code execution and persistent access. MITRE ATT&CK Mapping:
- T1190 - Exploit Public-Facing Application
- T1505.003 - Web Shell deployment
- T1078 - Valid Accounts (compromised credentials)
- T1552.004 - Private Keys (ASP.NET machine key theft)
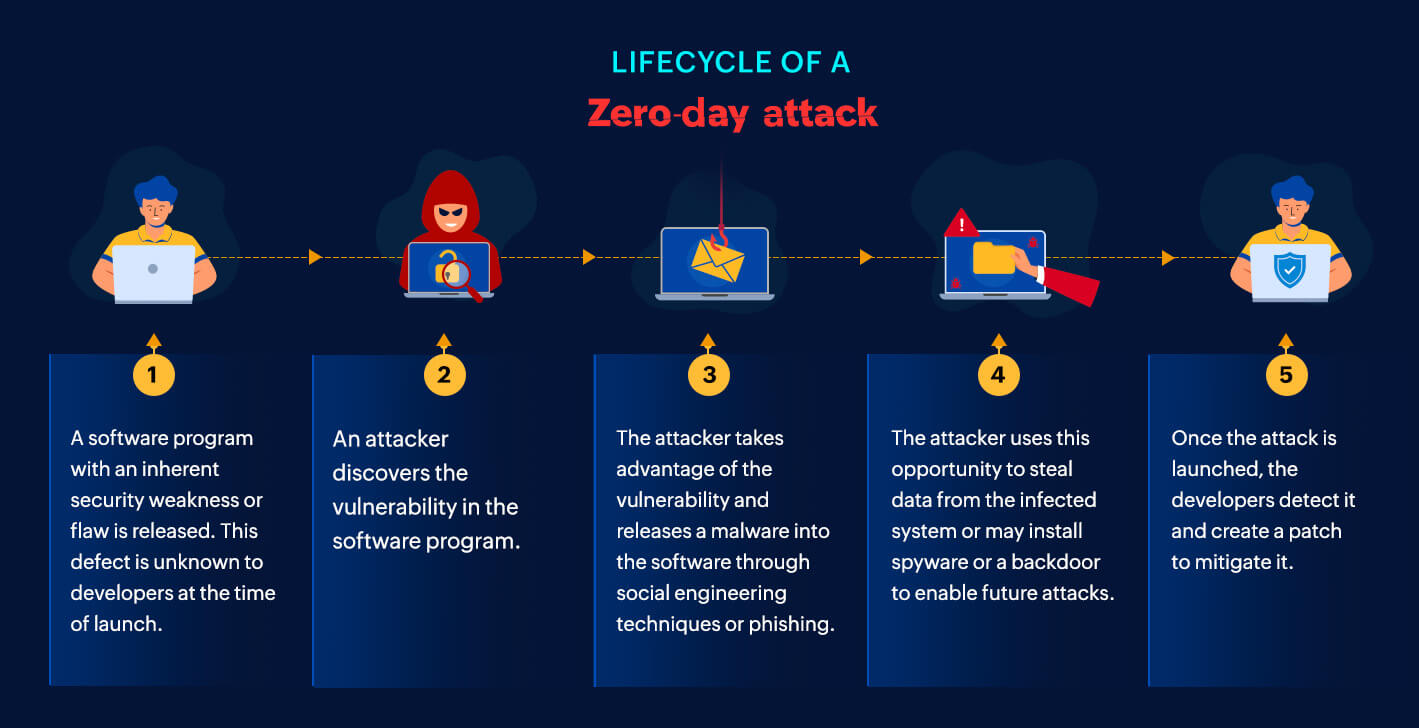
4. FIDO Authentication Research Clarification
Research Timeline: July 21-26, 2025 Initial Claim: PoisonSeed campaign bypassed FIDO hardware key protections Retraction: July 25-26, 2025 - Expel confirmed MFA challenges failed, no actual bypass occurred Technical Reality: Cross-device authentication flow properly rejected unauthorized attempts Security Research Implications: The FIDO research retraction highlights the importance of thorough verification in security research. While the PoisonSeed campaign successfully phished credentials and captured QR codes, the underlying FIDO2 protections remained intact, with all MFA challenges failing as designed.
Strategic Threat Intelligence Analysis
The July 26 incident landscape reveals three critical threat vectors reshaping organizational risk profiles. First, the insurance sector faces coordinated targeting by sophisticated threat actors, with Scattered Spider demonstrating persistent focus on social engineering techniques against cloud service providers. This represents a strategic shift from traditional network perimeter attacks to supply chain compromise methodologies.
Second, consumer application security continues to lag behind enterprise standards, particularly in biometric data protection. The Tea dating app breach exemplifies inadequate security controls around sensitive personal data, creating cascading privacy risks through potential deepfake creation and identity theft vectors.
Third, state-sponsored actors demonstrate accelerating capabilities in zero-day exploitation and patch analysis. The SharePoint campaign's rapid progression from incomplete patch to global exploitation within hours indicates advanced reverse engineering capabilities and coordinated infrastructure deployment by China-linked APT groups.
The convergence of these threat vectors suggests organizations must prioritize third-party risk management, biometric data governance, and accelerated patch deployment cycles to maintain defensive posture against evolving attack methodologies.
CISO Strategic Recommendations
1. Implement Enhanced Third-Party Risk Management - Deploy continuous monitoring of cloud service provider security postures with contractual security requirements and incident response coordination protocols.
2. Strengthen Social Engineering Defenses - Establish multi-channel verification procedures for high-privilege access requests and implement behavioral analytics for anomalous authentication patterns.
3. Accelerate Patch Management Cycles - Deploy automated patch testing and deployment pipelines with emergency response procedures for zero-day vulnerabilities affecting critical infrastructure.
4. Enhance Biometric Data Protection - Implement encryption-at-rest and data minimization policies for biometric verification systems with regular security assessments of consumer-facing applications.
5. Deploy Advanced Threat Hunting - Establish proactive threat hunting capabilities focused on APT tactics, techniques, and procedures with emphasis on collaboration platform monitoring and anomalous cross-device authentication patterns.
Threat Landscape Analysis
The current threat landscape demonstrates a fundamental shift toward supply chain compromise and third-party infrastructure targeting. State-sponsored actors increasingly focus on collaboration platforms like SharePoint, recognizing their central role in organizational data flows and privileged access management. The rapid exploitation of incomplete patches indicates sophisticated reverse engineering capabilities and coordinated attack infrastructure deployment.
Consumer application security remains a critical vulnerability, with dating apps and social platforms presenting attractive targets for personal data harvesting and identity theft operations. The intersection of biometric data collection and inadequate security controls creates long-term privacy risks extending beyond immediate breach impacts.
Insurance sector targeting represents a strategic focus on high-value data repositories and financial services infrastructure. The attribution of multiple recent breaches to Scattered Spider suggests coordinated campaign planning and persistent access maintenance across the sector.
Organizations must adapt defensive strategies to address these evolving threat vectors through enhanced third-party risk management, accelerated patch deployment, and comprehensive monitoring of collaboration platforms and consumer-facing applications.
Conclusion and Forward-Looking Insights
The July 26, 2025 breach landscape underscores the critical importance of comprehensive third-party risk management and rapid response capabilities. The Allianz Life incident demonstrates how sophisticated threat actors exploit trust relationships between organizations and cloud service providers, while the Tea dating app breach highlights persistent vulnerabilities in consumer application security.
Looking forward, organizations must prepare for continued state-sponsored exploitation of collaboration platforms and increased targeting of biometric data repositories. The insurance sector's ongoing exposure to Scattered Spider campaigns suggests coordinated threat actor focus on high-value financial services data.
CISOs should prioritize investment in automated threat detection, third-party security monitoring, and incident response coordination with cloud service providers. The rapid evolution from incomplete patches to global exploitation demands accelerated security update deployment and comprehensive vulnerability management programs.
The convergence of state-sponsored capabilities, criminal threat actor sophistication, and expanding attack surfaces requires adaptive security architectures capable of defending against multi-vector campaigns targeting both enterprise infrastructure and consumer privacy.
Sources and References
1. TechCrunch - "Allianz Life says 'majority' of customers' personal data stolen in cyberattack" (July 26, 2025)
2. Reuters - "Women's dating app Tea reports 72,000 images stolen in security breach" (July 26, 2025)
3. The Hacker News - "PoisonSeed Attack Turns Out to Be Not a FIDO Bypass After All" (July 21-26, 2025)
4. CSO Online - "Microsoft's incomplete SharePoint patch led to global exploits by China-linked hackers" (July 24, 2025)
5. CISA - Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog (CVE-2025-53770)
6. Microsoft Security Response Center - SharePoint Server Security Updates (July 2025)
7. National Vulnerability Database - CVE-2025-53770, CVE-2025-53771











.webp)
/image1.jpeg?profile=RESIZE_930x)
/image2.jpeg)
/image3.jpeg)

 Professional visualization of ransomware attack on IT distribution infrastructure
Professional visualization of ransomware attack on IT distribution infrastructure