In the realm of cybersecurity, the ability to respond swiftly and effectively to a crisis is paramount. For organizations, especially those entrusted with securing government data and infrastructure, the stakes are incredibly high. That's where cyber crisis drills come into play. In this Fireside chat, our speakers, Dan Lohrmann and Bikash Barai, delve into the nitty-gritty of running cyber crisis drills for the US government and Homeland Security.
Meet the Experts
Dan Lohrmann is the Chief Security Officer and Chief Strategist at Security Mentor. With a background at the National Security Agency and experience as a former CISO for the State of Michigan, Dan brings a wealth of knowledge in cybersecurity to the table.
Bikash Barai is one of the co-founders of FireCompass and CISO Platform, a cybersecurity community. His expertise in cybersecurity, particularly in the realm of red teaming, adds a unique perspective to the conversation.
Before we dive into the tactics, it's worth noting that this is Part 3 of a 4-part discussion. If you haven't checked out the previous parts yet, you can catch up here:
- Part1: Running Cyber Crisis Drills For The US Government With Dan Lohrmann & Bikash Barai
- Part2: Preparing for the Unpredictable and Scenario Based Drills for the US Government & Homeland Security With Dan Lohrmann & Bikash Barai
Do's and Don'ts for Successful Cyber Crisis Drills
Preparation is Key
One of the fundamental pillars of conducting successful cyber crisis drills is thorough preparation. This entails providing participants with read-ahead materials that simulate real-life scenarios. These scenarios could be based on incidents at other companies, competitors, or industry-specific challenges. It's essential to equip your team with intelligence, even if it's not a real situation. This could involve briefing them on current events relevant to your industry, such as economic shifts or emerging threats.
Change It Up
One common pitfall in cyber crisis drills is complacency. To keep participants on their toes, consider throwing curveballs into the mix. Surprise your team by making sudden changes, like reassigning roles or introducing unexpected scenarios. This not only tests their adaptability but also ensures they don't become too comfortable with routine responses. The real world is full of surprises, and preparedness means being ready for the unexpected.
Actionable Items
At the end of a crisis drill, it's not enough to wrap up and move on. The key is to identify actionable items. Assign responsibilities for each item, and ensure there is a clear owner. Make it a point to report back on these items, whether through email updates or, ideally, a follow-up meeting. This level of accountability helps drive improvements and ensures that lessons learned are translated into real-world action.
Seek Feedback
Constructive feedback is invaluable. After the drill, conduct a "hot wash" or a feedback session where participants can share their thoughts, ideas, and concerns. You can use surveys to gather feedback or have an open discussion. Encourage your team to think outside the box and challenge the status quo. Valuable insights can often emerge from these discussions, leading to refined strategies.
Step Out of the Comfort Zone
Sometimes, hosting a drill within the same familiar environment may lead to complacency. To maintain engagement and focus, consider taking your team to an off-site location. This approach removes the distractions of daily work routines, encouraging participants to fully immerse themselves in the exercise. It's a small change that can make a significant difference.
The Ever-Changing Landscape of Cybersecurity
As we look ahead to 2021, it's crucial for cybersecurity professionals to remain vigilant. The landscape is continually evolving, and staying prepared is an ongoing journey, not a destination. Here are a few trends and areas of focus for the year:
Ransomware Evolution
Ransomware attacks are becoming increasingly complex and sophisticated. Attackers not only encrypt data but may also steal it before applying encryption. This double-threat strategy puts added pressure on organizations to pay the ransom, as the threat of data leakage looms.
Remote Work Challenges
The shift towards remote work, accelerated by global events, presents new challenges. Home networks have become prime targets for hackers, and organizations must adapt to secure their remote workforce effectively.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are playing a more central role in cybersecurity. They not only help in threat detection but are also being used by attackers. Automating processes is crucial to stay ahead in the game.
Cloud Security
As more businesses migrate to cloud platforms, the responsibility for end-to-end security remains with the organization. Don't assume that cloud providers have you fully covered. Cloud security is a shared responsibility.
Zero Trust and SASE
Implementing a Zero Trust model and exploring Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) solutions can enhance security in an environment where traditional network boundaries are blurred.
>>For Part 4 of the Blog Read Here
>>To stay updated on the latest cybersecurity trends and insights, consider joining CISO Platform, the cybersecurity community. You can sign up here: Join CISO Platform.
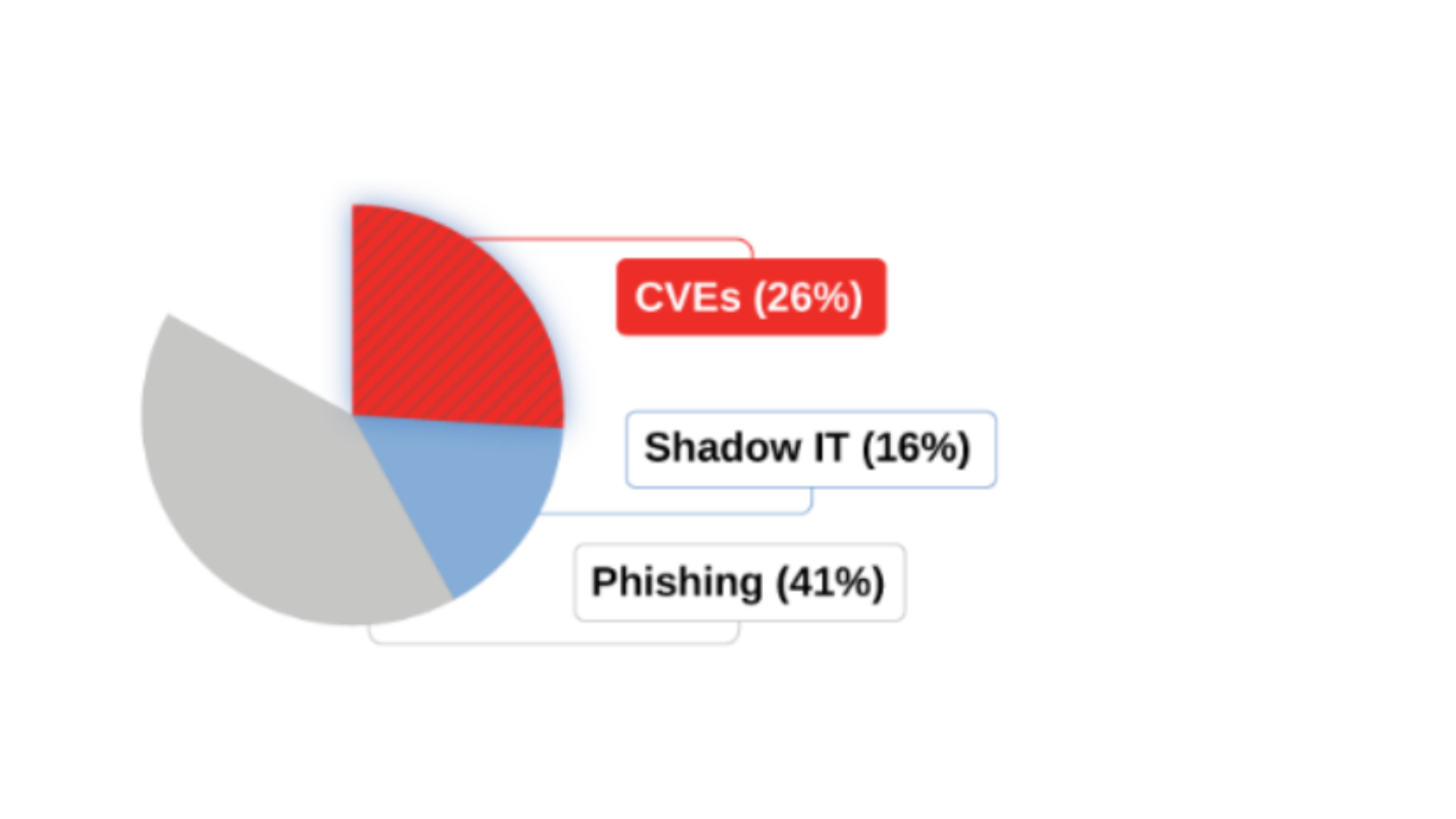
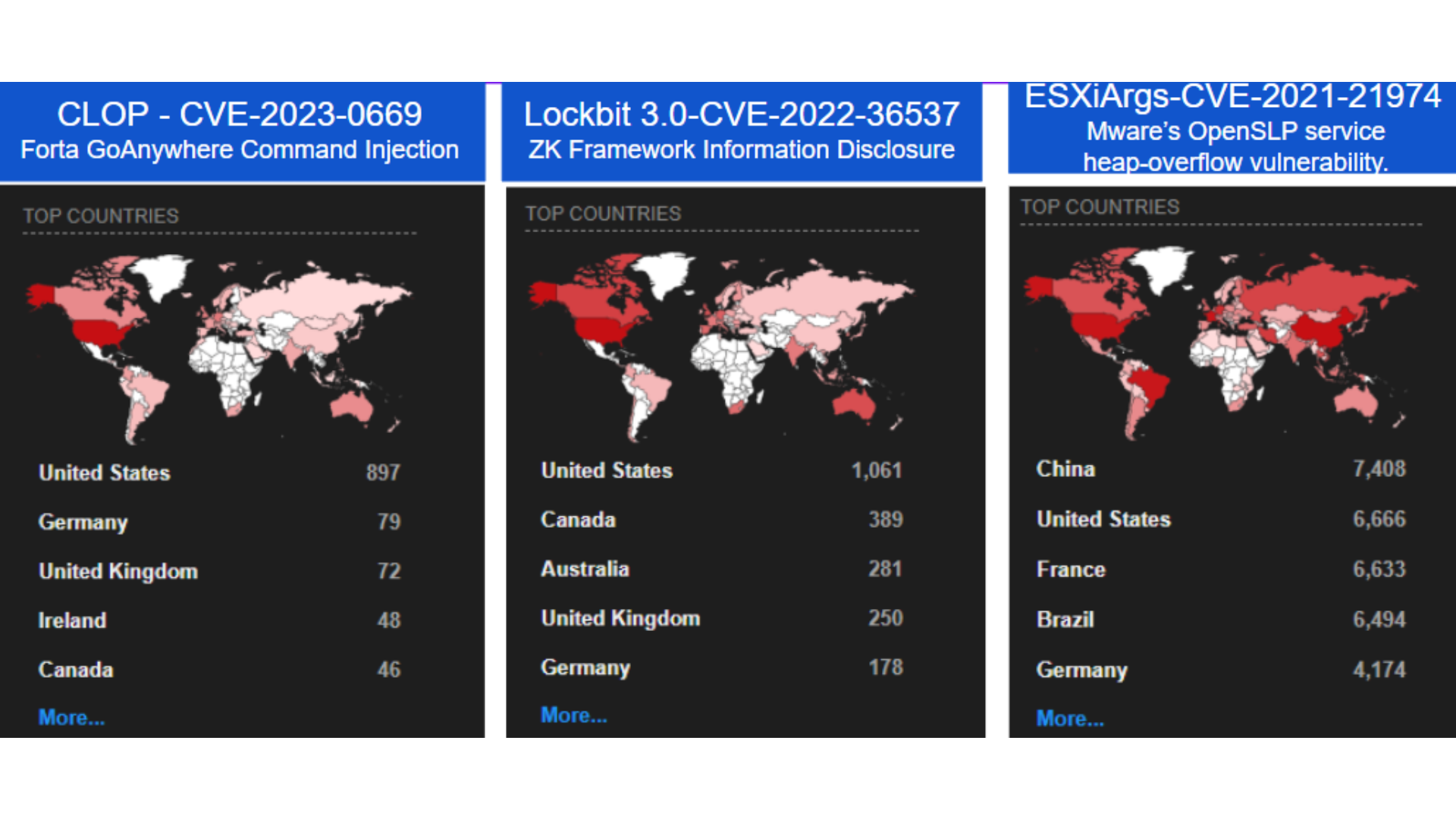
.png?profile=RESIZE_710x)