We're talking about the latest Java-based vulnerability CVE-2021-44228. Recently, a critical Zero-day vulnerability has been found in log4j which permits Remote Code Execution (RCE) allowing the attackers to get remote access. The Vulnerability got a severity score of 10 out of 10 and several national cybersecurity agencies, including CISA, NCSC and others have issued warnings and emphasized that organizations must “discover unknown instances of Log4j” in addition to patching.
CVE-2021-44228 impacts any organization using Apache Log4j framework including Apache Struts2, Apache Solr, Apache Druid, Apache Flink, and others.
>> Discover log4j exposure (by FireCompass)
About The Log4j vulnerability :
According to the National Vulnerability Database, “Apache Log4j2 2.0-beta9 through 2.12.1 and 2.13.0 through 2.15.0 JNDI features used in configuration, log messages, and parameters do not protect against attacker controlled LDAP and other JNDI related endpoints.” An attacker can execute arbitrary code loaded from LDAP servers when message lookup substitution is enabled.
From log4j 2.15.0, this behavior has been disabled by default. From version 2.16.0, this functionality has been completely removed. However, this vulnerability is specific to log4j-core and does not affect log4net, log4cxx, or other Apache Logging Services projects.
The Impact of Log4j vulnerability:
Just to put it in perspective, the scan result of Maven Central by Google's Open Source Insights Team, found that almost 8% of packages in the repo have at least one version that is affected by the log4j vulnerability.
Within a week of the exposure of the vulnerability, more than 1 million attacks were attempted and more than 44% of corporate networks worldwide were targeted. And this is just the beginning - the worst of the cyber attacks may actually be months into the future since sophisticated attackers normally create a backdoor, steal credentials and try to bypass security tools and wait for the right time to strike. The nation state-backed hacking groups are also spotted attempting to leverage Log4j.
>> Discover log4j exposure (by FireCompass)
How to Protect :
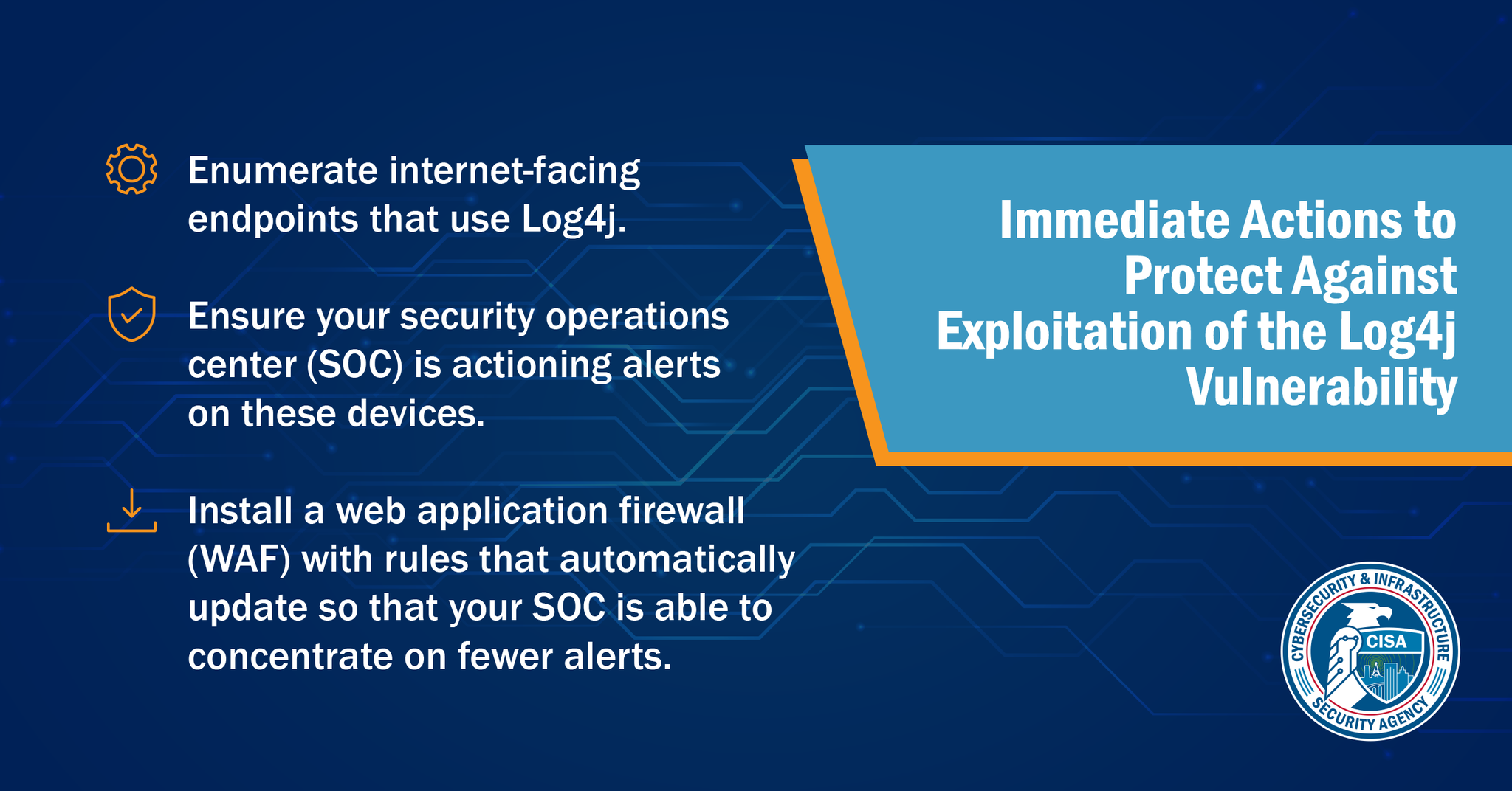
CISA recommends all organizations upgrade to log4j version 2.15.0 or complete their appropriate vendor recommended mitigation along with the following steps:
- Enumerate any external facing devices that have log4j installed*
*Note: Check for platforms that can hunt Log4j vulnerabilities in both known & shadow IT assets
- Make sure that your security operations center is actioning every single alert on the devices that fall into the category above.
- Install a web application firewall (WAF) with rules that automatically update so that your SOC is able to concentrate on fewer alerts.
>> Discover log4j exposure (by FireCompass)
Some Important Updates :
You can try to determine whether your organization's products with Log4j are vulnerable by following the chart below:
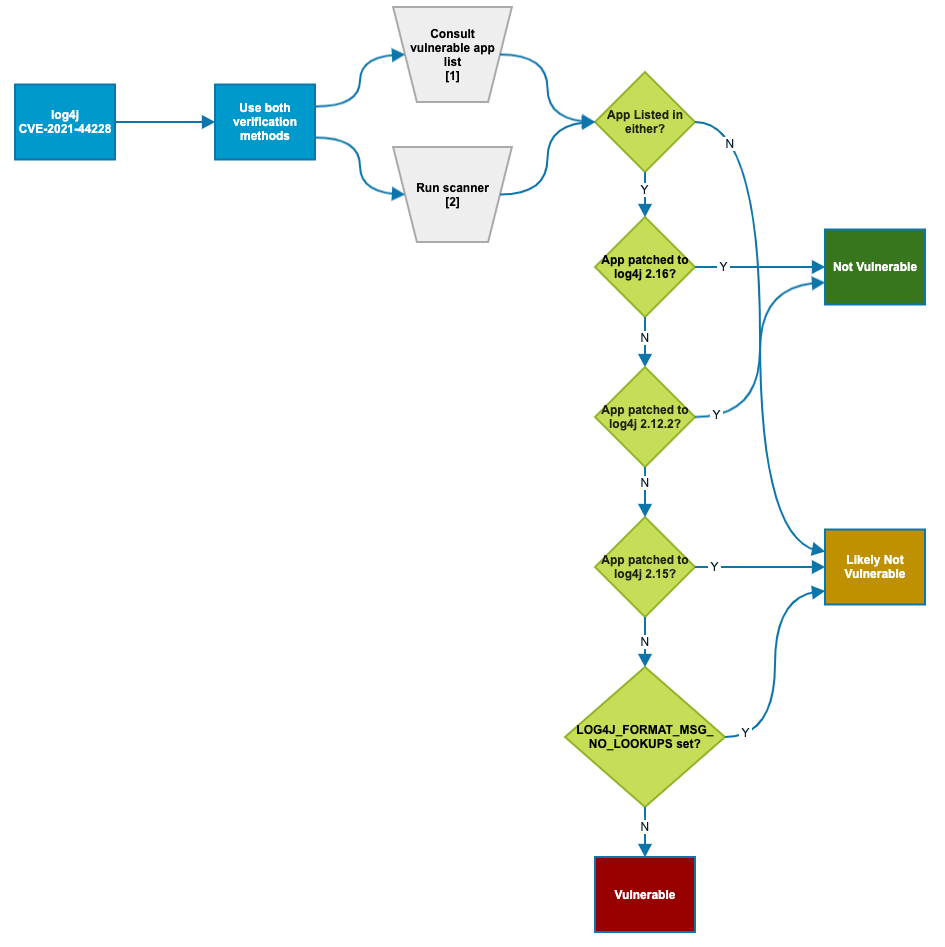
While we are writing this article, the Apache Software Foundation has released a patch for a third vulnerability in Log4j. Version 2.17.0 of the software was released on December 17 after issues were discovered with the previous release (2.16). Apache said that 2.16 does not always protect from infinite recursion in lookup evaluation and is vulnerable to CVE-2021-45105, a denial of service vulnerability.
Important Resources:
%20The%20Challenge%20Of%20CISO%20Burnout.png?profile=RESIZE_400x)

