pritha's Posts (583)
We are excited for the next ‘Best Of The World’ Session On "Understanding Cloud Attack Vectors" by Moshe Ferber (Cloud Security Expert, Frequent Speaker at Defcon, Blackhat, RSAC APJ)
The 'Best Of The World' Series features the world's best security minds (researchers, inventors, subject experts, analysts). It covers security content and Q&A that is often hard to comprehend and you simply cannot ‘Google it’. It has featured great minds like Paul Raines (Nobel prize winner), Jacob Torrey (DARPA), Dr. Phil Polstra (Renowned Forensic Expert, BlackHat).
Key Discussion Points :
- Understanding current cloud threats landscape
- Reviewing cloud attack vectors
- Recent examples of cloud security incidents
- Prioritize cloud security efforts
You can join us here: https://info.cisoplatform.com/understanding-cloud-attack-vectors?utm_src=CPblog
Please Note : Since the speakers are across the globe (best of the world in security), the timings might be odd. In case the time does not suit your timezone, kindly register yourself, so you can get access to the recording post-session.
This webinar covers various aspects, including the rise in cyber security incidents, identification of vulnerabilities and loopholes, effective prevention strategies, mitigation techniques, and more. It aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the evolving cybersecurity landscape in the context of Web3 technologies.
Key Discussion Points
- Discuss Security Incidents & Business Use Case
- Understanding Web 3 Pros
- Understanding Web 3 Cons. Prevention mechanism
- How to make sure that it doesn’t happen to you?
About Speaker
Gregory Pickett is a Blackhat USA Speaker, CISSP, GCIA, GPEN. He is the founder and Head of Cybersecurity Operations for Hellfire Security. He has presented research at over seventeen international conferences. He is a Six-time speaker at Defcon and three-time speaker at Blackhat.
(Webinar) Recorded
Discussion Highlights
1. Common Attacks
- Price Oracle Manipulation
- Improper Access Control
- Improper Validation and Logic Errors
- MEV Attacks (Front Running, Sandwiches)
- Traditional Methods :
SIM Swapping, Phishing Attacks, Vulnerable Nodes, Abused Permissions, Abused Network
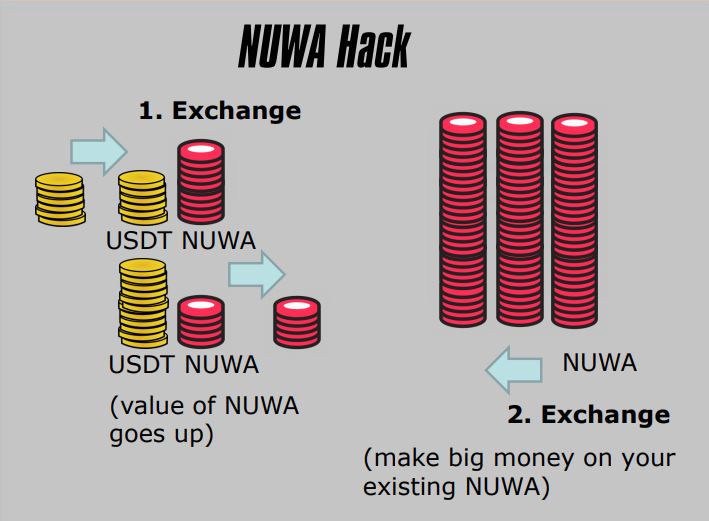
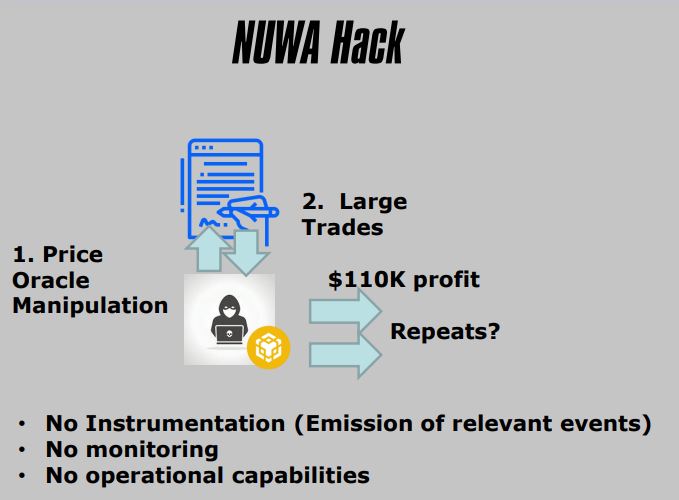
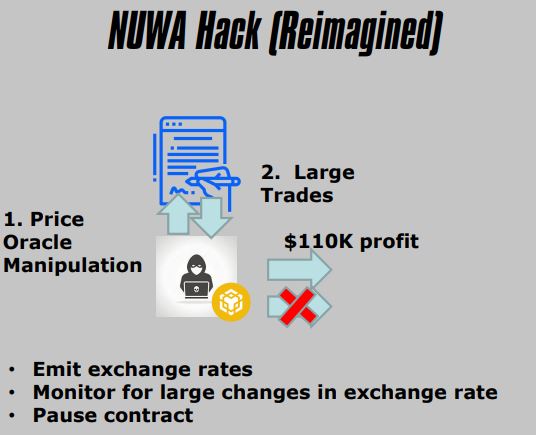
2. NUWA Hack
- ERC-20 Token
- Price Oracle Manipulation
- Publicly Known
- Liquidity Pool Imbalance
- Distorted Exchange Rate
- Used to Exchange At A Favorable Rate
3. Important Events/States To Emit
- Low Balances
- Liquidity Pool Ratios (Or Exchange Rates)
- Change in Ownership
- Funds Distributions
- Attributes Generated
- Wins/Losses
4. Important Operational Capabilities
- Blacklist Wallets
- Transfer Pools
- Pause Contract
- Kill Contract
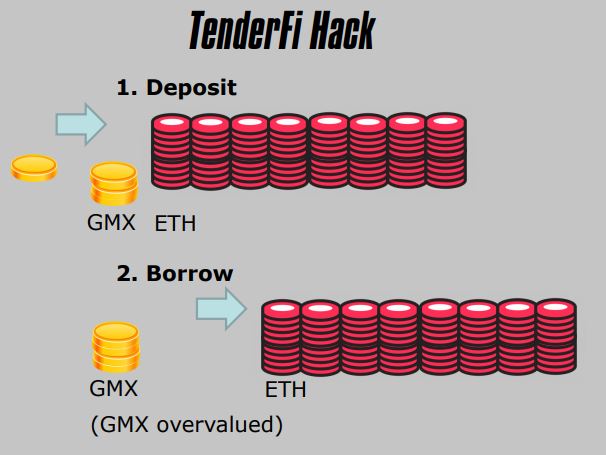
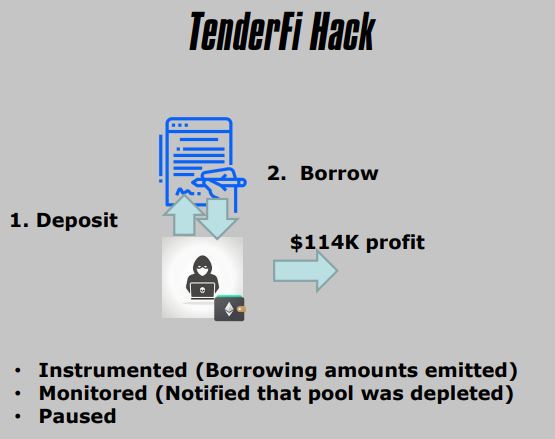
5. TenderFi Hack
- DeFi Platform
- Price Oracle Misconfiguration
- Publicly Known
- Implicit Decimal Point
- Overvalued Token
- Produced a very favorable loan (larger than total value of all Bitcoin)
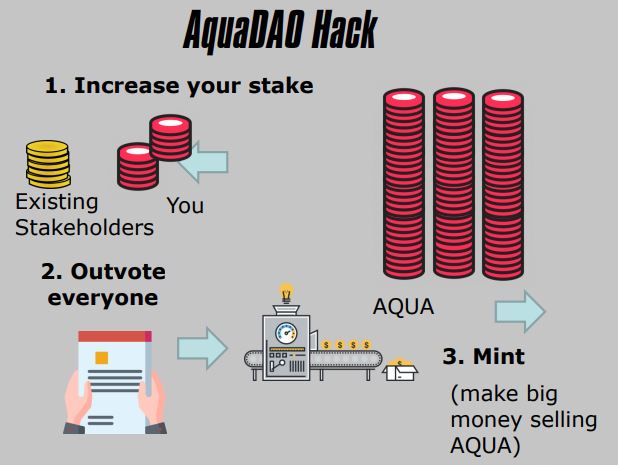
6. AquaDAO Hack
- Decentralized Autonomous Organization
- Governance Attack
- Insufficient Stake
- Malicious Proposal
- Destroyed Value
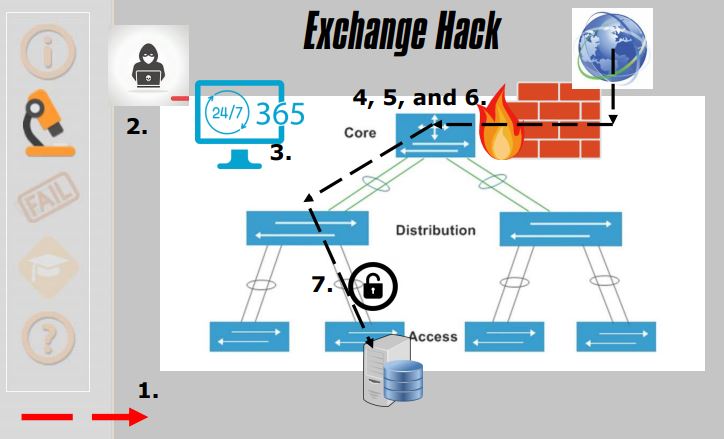
7. Exchange Hack
- Hot Wallet
- Abused Privileges
- Not Public
- No Privileged Access Management
- No Compensating Controls
- Transferred Funds Out of Hot Wallet
- Drained Hot Wallet
- No Privileged Access Management
- No Log Aggregation
- No Monitoring of Login/Logout Events
- No Access Attestation
- Enterprise Network
- Abused Network
- Not Public
- No Zoning, No Hardening, and No Governance
- No Compensating Controls
- All Customer Data include OTP Seeds
- Wouldn’t you like to know
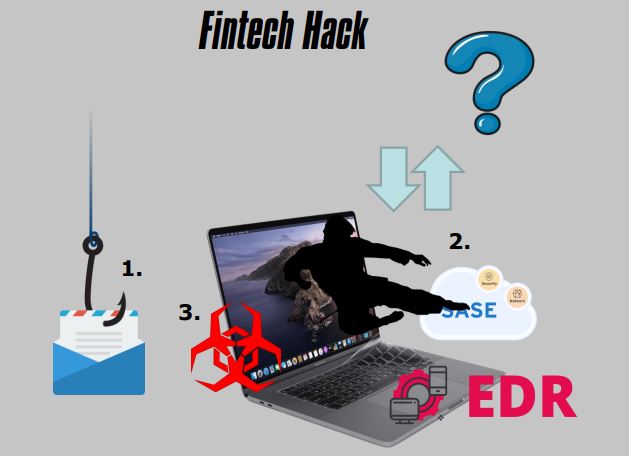
8. Fintech Hack
- Key Engineer
- Phishing Attack
- Not Public
- Lacking Cybersecurity Fundamentals
- Buying Products to Solve Problems
- Who Knows
- No Security Awareness Training
- No SIEM Tuning
- No Flow Monitoring
- No Privileged Access Management
9. Buying Products (or Services) to Solve Problems
- Protecting Users (EDR)
- Protecting Network (SASE)
- Monitoring Activity (SIEM)
- Secure Software (SSDLC) (Audit Services)
10. Hope Is Not A Strategy
- They Are Looking for the Perfect Products
- If we have the right X/Y/Z, we will never have to worry about threats
- Web3 Itself Is Seen In A Similar Fashion
- Just Perform More Audits
(PPT) Presentation From The Discussion
We are excited for the next ‘Best Of The World’ Session On "How To Create Scalable And Sustainable Cybersecurity Program For Any Size Organization" by Gordon Rudd, (Ex-CISO RCB Bank | Author | Coach)
The 'Best Of The World' Series features the world's best security minds (researchers, inventors, subject experts, analysts). It covers security content and Q&A that is often hard to comprehend and you simply cannot ‘Google it’. It has featured great minds like Paul Raines (Nobel prize winner), Jacob Torrey (DARPA), Dr. Phil Polstra (Renowned Forensic Expert, BlackHat).
Key Discussion Points :
- Understand the relationship between the cybersecurity and IT Operations
- Assess organizational cybersecurity, GRC & operational readiness
- Successfully communicate with the C-Suite and the Board on the state of cybersecurity in the organization
- Identify and focus on the top five areas needed in building real world cyber defenses
You can join us here: https://info.cisoplatform.com/creating-scalable-sustainable-cybersecurity-for-any-size-organization?utm_src=cpblog
Please Note : Since the speakers are across the globe (best of the world in security), the timings might be odd. In case the time does not suit your timezone, kindly register yourself, so you can get access to the recording post-session.
Over 18 years, RSAC Innovation Sandbox contest brings cybersecurity's new innovators to put the spotlight on their potentially game-changing ideas. Each year, 10 finalists grab the spotlight for a three-minute pitch while demonstrating groundbreaking security technologies to the broader RSA Conference community. Since the start of the contest, the top 10 finalists have collectively seen over 75 acquisitions and $12.48 billion in investments. (Source : RSA Conference)
"Innovation And Security converge on the floor of RSA Conference 2023!"
Top 10 Finalists Sandbox 2023
AnChain.AI
AnChain.AI (www.anchain.ai) is an AI-powered cybersecurity company enhancing blockchain security, risk, and compliance strategies. Blockchain Xcelerator.
Astrix Security
Astrix provides holistic visibility into all non-human connections and identities - automatically detects and remediates over-privileged, unnecessary, misbehaving and malicious app-to-app connections to prevent supply chain attacks, data leaks and compliance violations.
Dazz
Dazz is a cloud security company specializing in protecting cloud development environments. The platform helps solve vulnerabilities and prevents risks in cloud development environments.
Endor Labs
Endor Labs offers a dependency lifecycle management tool that facilitates the security and maintenance of Open Source Software.
Hidden Layer
HiddenLayer’s patent-pending solution provides a noninvasive, software-based platform that monitors the inputs and outputs of your machine learning algorithms for anomalous activity consistent with adversarial ML attack techniques. Response actions are immediate with a flexible response framework to protect your ML.
Pangea
Pangea Cyber wants to change that with an API-driven approach to adding security to an application, making it as easy as adding a few lines of code.
Relyance
Manage privacy, data governance, and compliance operations seamlessly, all on a single, intuitive platform.
SafeBase
The Smart Trust Center for sharing your security posture and automating access to sensitive documents.
Valence Security
Valence Security collaboratively remediates SaaS data, supply chain and identity risks through automated policy enforcement.
Zama
Advancing Homomorphic Encryption for a More Private Internet
Judges
- Niloofar Razi Howe, Sr. Operating Partner, Energy Impact Partners
- Paul Kocher, Researcher, Independent Researcher
- Shlomo Kramer, Co-founder and CEO, Cato Networks
- Barmak Meftah, Co-founder and Partner, Ballistic Ventures
- Executive Vice-President, Bus Dev, Strategy and Ventures, Microsoft
We had a community webinar on "From Chaos To Control : Lessons Learned From The Ransomware Attack". We discussed the importance of cybersecurity and the growing threat of ransomware attacks. Described the specific incident we experienced, highlighting the impact on our organization and the challenges we faced. Key lessons we learned from the incident, including what worked well and what could have been done differently. Emphasize the importance of having a comprehensive backup and employee training.
Session Agenda
- Importance of having a comprehensive incident response plan
- Need for regular backups and employee training
- Best practices for preventing ransomware attacks
- Need for ongoing monitoring and testing of security measures to ensure they are effective and up to date
- Importance of learning from the experience and continually improving security measures to stay ahead of evolving threats
About Speaker
Prabhakar Ramakrishnan, CISO & General Manager - IT Infrastructure at TNQ Technologies
(PPT) Presentation From The Discussion
Discussion Highlights
1. Growing Threat of Ransomware Attacks
- Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts files on a victim's computer system, making them inaccessible until a ransom is paid
- The threat of ransomware attacks is growing as cybercriminals are becoming more sophisticated and using new tactics such as double extortion, where they not only encrypt the victim's data but also threaten to leak it if the ransom is not paid
2. Impact of Ransomware Attacks
- Ransomware attacks can have a devastating impact on individuals and organizations, causing financial losses, reputational damage, and even legal liabilities
- In addition to the direct costs of paying the ransom and restoring the encrypted data, there are also indirect costs such as lost productivity, business interruption and regulatory compliance
3. Personal experience and lessons learned :
Backup - RPO : 2hours, 8hours, 24hours
Incident Response Plan
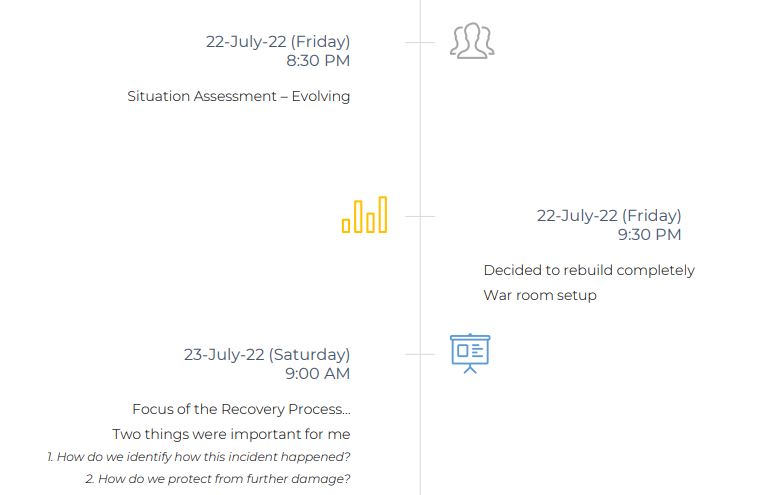
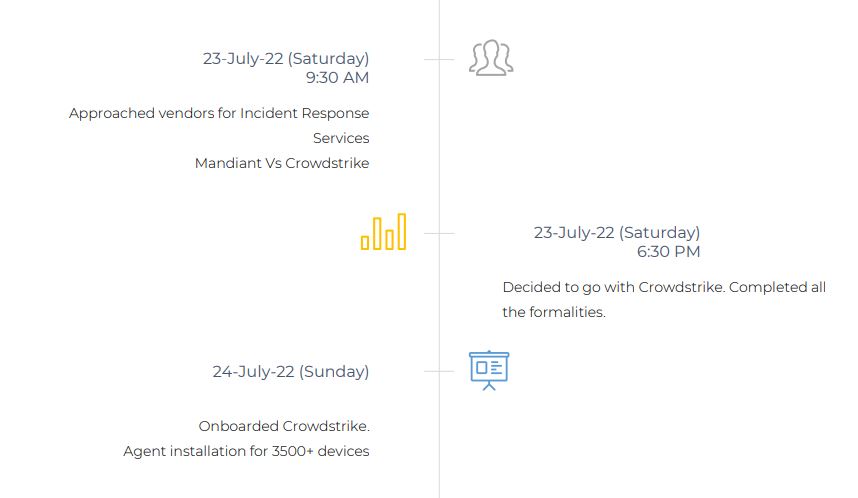
4. How we recovered
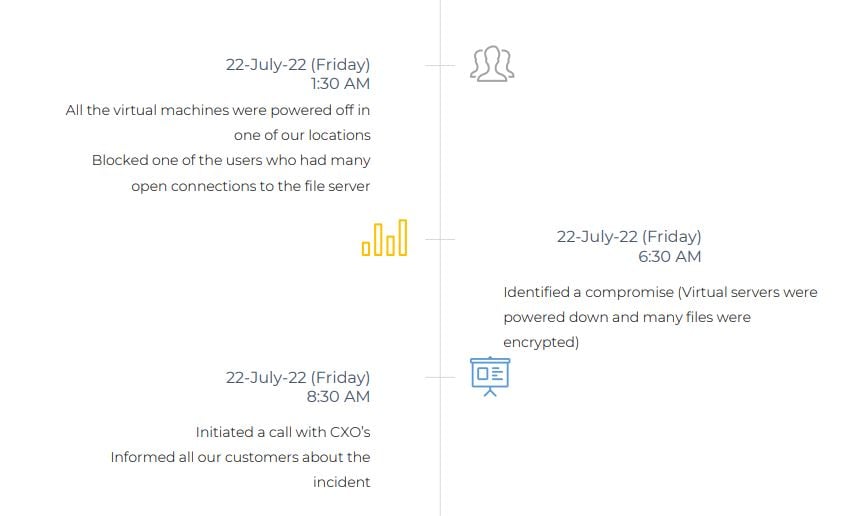
5. Incident Summary
- Threat actor used a compromised account to access the servers over RDP
- Using the Admin account the Threat actor copied and installed an open-source softwarefor anonymous communication named TOR (The Onion Router). During this installation, Threat Actor masqueraded the anonymity software TOR as Applocker.exe which is a legitimate Microsoft Windows application
- TOR is an open-source software that creates a multi-hop proxy network which allows Threat Actors to communicate with the installed systems over an encrypted channel
- To further maintain persistence in the environment, the Threat Actor installed multiple remote management software like Atera agent, AnyDesk, LogMeIn and BitVise and ZeroTier
- Threat Actor attempted to perform lateral movement by installing the Remote Management tool named Action1
- Threat Actor used the compromised privileged account to copy a compressed file which contained multiple legitimate system administration tools, different variants of ransomware encryptor and text files
- Threat Actor created an account MS_BACKUP on the Domain controller and added the Account Domain Admin Group
6. Ransomware Deployment Activity
- The Threat Actor copied multiple binaries of Windows and Linux based ALPHV ransomware encryptors to the system
- The Threat Actor targeted ESXi systems by copying the Linux ALPHV ransomware executable and linkable format (ELF) binaries on multiple VMware ESXi systems
- Once connected to the ESXi systems through SSH connections using the root account, the Threat Actor copied over the ALPHV ELF binary encryptor to the ESXi systems and executed the ransomware encryptor. This resulted in the encryption of several virtual machine disk (VMDK) files stored on the datastore attached to these ESXi systems
7. Major Gap’s
- EDR was not installed in the servers that were compromised
- Weak password, Same password used for multiple devices
- 2FA was not configured for all external facing applications
- Backups stored in the same environment
- Lack of centralized logging
8. Important Documents
- Situational Awareness Report
- Communication Plan
- Recovery Process
We are excited for the next ‘Best Of The World’ Session On "Impacts of Web3 on Cybersecurity : Cyber Security Incidents; Loopholes; Prevention; Mitigation & More" by Gregory Pickett (Blackhat USA Speaker, CISSP, GCIA, GPEN, Head of Cybersecurity Operations, Hellfire Security)
The 'Best Of The World' Series features the world's best security minds (researchers, inventors, subject experts, analysts). It covers security content and Q&A that is often hard to comprehend and you simply cannot ‘Google it’. It has featured great minds like Paul Raines (Nobel prize winner), Jacob Torrey (DARPA), Dr. Phil Polstra (Renowned Forensic Expert, BlackHat).
Key Discussion Points :
- Discuss Security Incidents & Business Use Case
- Understanding Web 3 Pros
- Understanding Web 3 Cons. Prevention mechanism
- How to make sure that it doesn’t happen to you ?
You can join us here: https://info.cisoplatform.com/stories-from-the-web3-battlefield-a-hackers-point-of-view?utm_src=cpblog
Please Note : Since the speakers are across the globe (best of the world in security), the timings might be odd. In case the time does not suit your timezone, kindly register yourself, so you can get access to the recording post-session.
We had “Best Of The World In Security” Webinar On "Analysing Cybersecurity Industry In Quarter 1". We discussed the latest analysis of the 3,251+ vendors in the cybersecurity industry. A bottoms up analysis of all the vendors derived from platform for industry research reveals the overall health of cybersecurity. Which companies and segments are growing and Which are failing Learnt how do these numbers compare to historical trends.
Session Agenda
- Zero signs of industry consolidation
- Digital Mercantilism is driving the growth in number of vendors
- Still no solution to the SolarWinds problem
About Speaker
Richard Stiennon is the Past VP Research, Network Security @Gartner, Author of Security Yearbook 2023. He is the Chief Research Analyst for IT-Harvest and has presented on cybersecurity in 29 countries in six continents, A Lecturer at Charles Sturt University and the Author of Surviving Cyberwar and There Will Be Cyberwar. Richard held leadership roles at Blancco Technology Group, Fortinet, Webroot Software and Gartner.
(Webinar) Recorded
Discussion Highlights
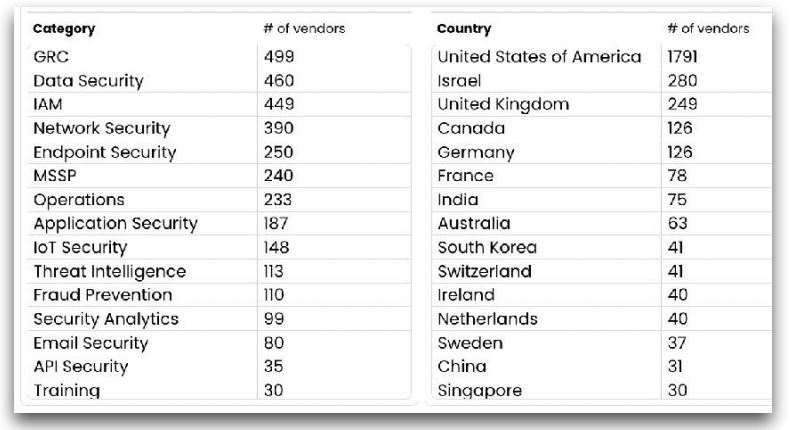
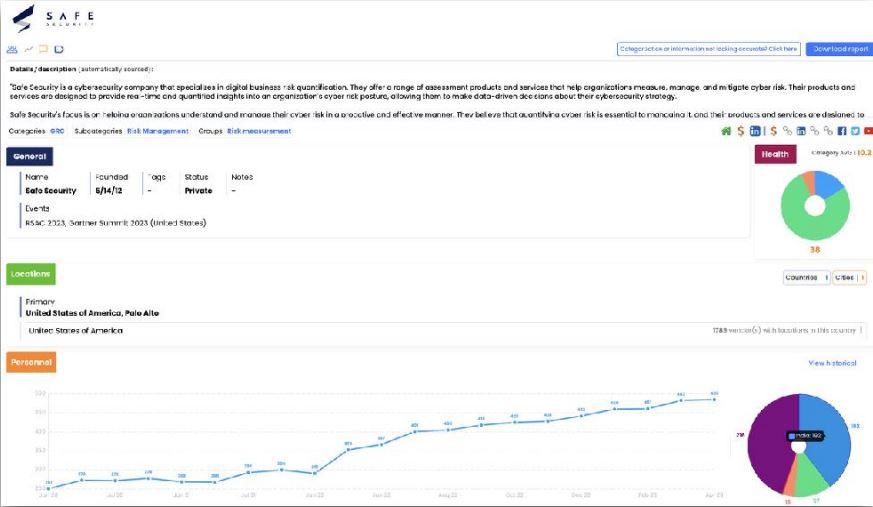
1. The vendor companies are categorization process & Industry experts. There are 3359 vendors company which create their own technology for security. The vendors are breakdown into categories by the country. The top 5 bucket of cybersecurity have always been - Government Risk Compliance (GRC), Data Security, Identity & Access Management (IAM), Network security, Endpoint Security.
There were 71 vendors that took in new capital. They were spread across 16 of the 17 categories we track, Deception was the one category with no new investments. As usual, the US led in funding rounds, followed by Israel and then the UK.
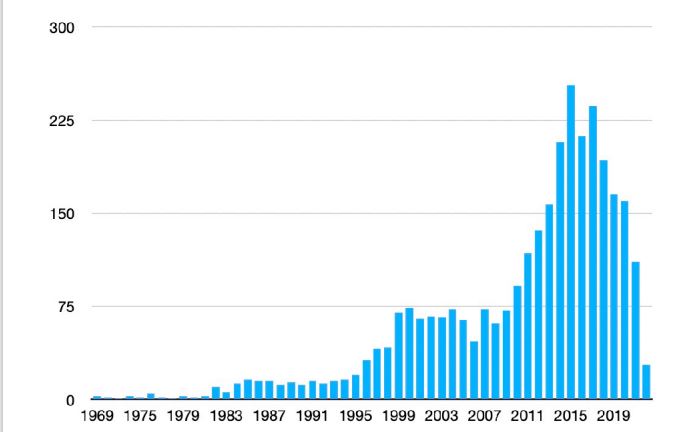
2. Vendors graph by founding dates, average date is 12 years.
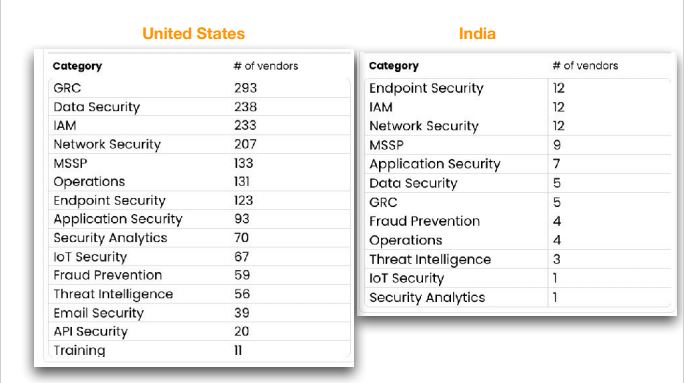
3. Vendors category Differences by Country
4. 50 more vendors are from India
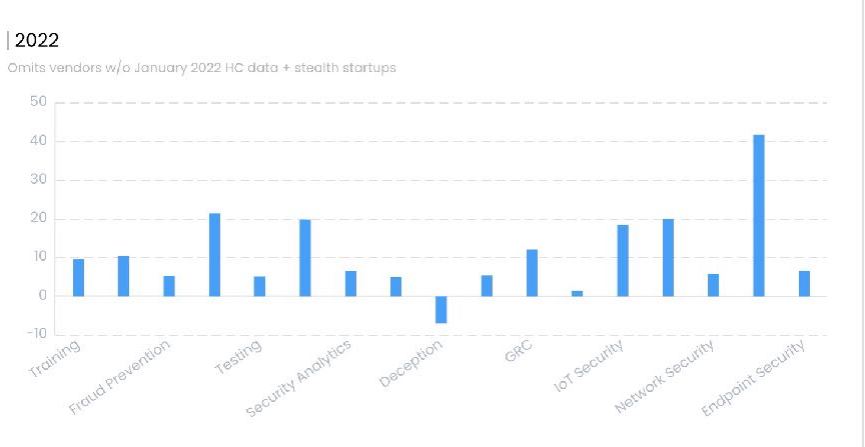
5. Growth by Sector, 2022
- Training
- Fraud Prevention
- Testing
- Security Analytics
- Deception
- GRC
- IOT Security
- Network Security
- Endpoint Security
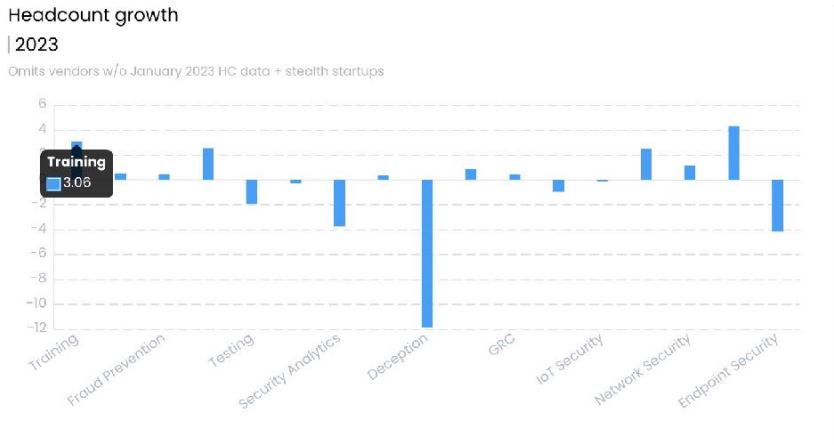
6. Growth by Sector, Quarter 1 2023
- Training
- Fraud Prevention
- Testing
- Security Analytics
- Deception
- GRC
- IOT Security
- Network Security
- Endpoint Security
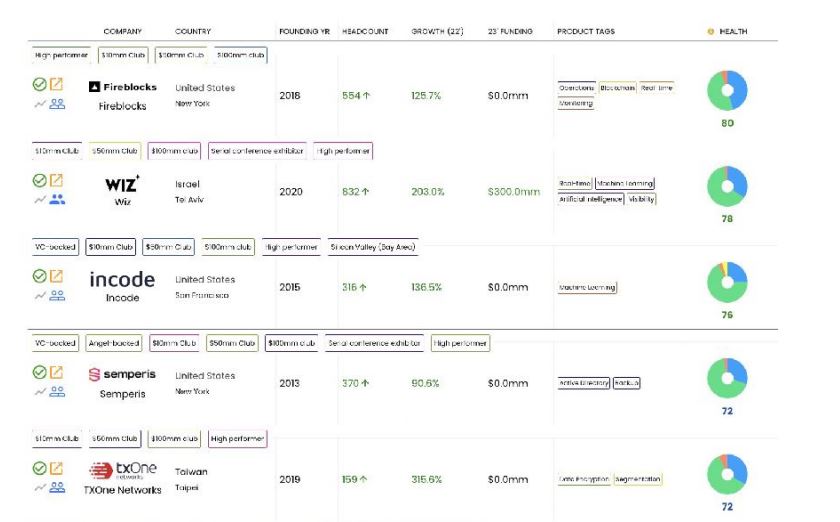
7. Fastest Growing Quarter 1, 2023
8. Investments - $17 billion 2022, while at $2.4 billion in Q1 on track to be under $10 billion in 2023. Last year saw 330 total investments, so Q1 is running at a lower annualized rate of 284. The top rounds below were all over $50 million, with NetSkope taking in the largest round of $401 million and Wiz taking in an additional $300 million at a $10 billion valuation.
9. Is the Industry Heading into a Recession?
- 54% of vendors grew in 2022
- 26% lost head count
- $17 billion is up 70% from 2020 level
- There were 338 acquisitions compared to 2021’s 415
Total funding was $2.413 billion, on track for a paltry $9.6 billion which will fall short of 2020’s $10 billion (which was a record at the time.) When I was a Gartner analyst we pegged the entire industry at a $2.2 billion market.One explanation for the short fall in new funding rounds could be that the March collapse of Silicon Valley Bank disrupted deal flow across the entire tech center. We will know if that is the case as Q2 plays out. An upswing in activity may be explained by delayed Q1 deals. (Reference link here)
We are excited for the next ‘Best Of The World’ Session On (Can't Google It | Best Of The World) Richard Stiennon (Past VP Research, Network Security @Gartner; Chief Research Analyst, IT-Harvest) On "Analysing Q1 Cybersecurity Industry" | CISO Session.
The 'Best Of The World' Series features the world's best security minds (researchers, inventors, subject experts, analysts). It covers security content and Q&A that is often hard to comprehend and you simply cannot ‘Google it’. It has featured great minds like Paul Raines (Nobel prize winner), Jacob Torrey (DARPA), Dr. Phil Polstra (Renowned Forensic Expert, BlackHat).
Key Discussion Points :
- Zero signs of industry consolidation
- Digital Mercantilism is driving the growth in number of vendors
- Still no solution to the SolarWinds problem
You can join us here: https://info.cisoplatform.com/q1-entire-cybersecurity-industry?utm_src=cpblog
Please Note : Since the speakers are across the globe (best of the world in security), the timings might be odd. In case the time does not suit your timezone, kindly register yourself, so you can get access to the recording post-session.
We had “Best Of The World In Security” Webinar On "DevOps Lesson For Your SOC (SRE)". We discussed Google-inspired lessons of transforming detection and response practices using the approach we call Autonomic Security Operations. DevOps transformed IT and changed roles, practices and skills within IT. Security in general and security ops, in particular, are sometimes left behind.
Session Agenda
- How does the security analyst role evolve?
- How security processes change in an ASO SOC?
- How automation reduces toil (and what is toil, anyway)
About Speaker
Dr. Anton Chuvakin, Past Gartner Analyst and very well known in the information security community. He is currently the security advisor at Office Of The CISO At Google Cloud. He is a recognized security expert in the field of SIEM, log management and PCI DSS compliance.
(Webinar) Recorded
Discussion Highlights
1. 2003 or 2023? Sec Ops is Ripe for Transformation
- We can’t store and analyze all data, resulting in blindspots
- It’s cost prohibitive to ingest all the data we need
- It takes too long to investigate alerts
- We struggle to build effective detection and have too many false positives/negatives
- Our processes are too manual, we are too slow to respond to and remediate threats
- We don’t have enough skilled engineers to make everything work
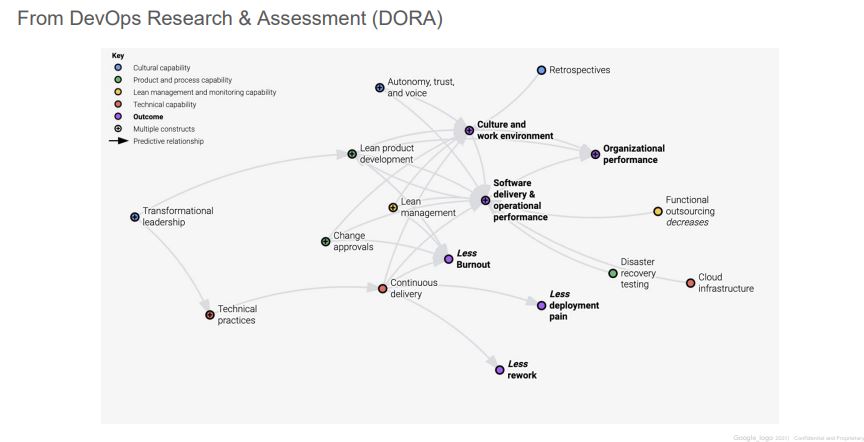
2. What Outcomes did DevOps / SRE achieve?
3. Google vs Enterprise “SecOps”
- What does Google do?
- Automation/SRE is a mindset – part of the hiring process, part of OKRs, and performance reviews
- Requires coding interviews, high pay, attracts the best, invests in growth
- 40/40/20 between eng, operations, and learning
- Investment in efficiency solves for human costs
- Intel strongly embedded in D&R, mostly utilized towards proactive work, strong collaboration across Alphabet & benefits from developer hygiene
- What do most enterprises do?
- Experimenting with SOAR, full adoption is tough due to minimal automation culture
- Hires traditional roles, no coding, rarely outsources, less pay, less growth, more stress
- Utilization is almost always >100%
- Cost-prohibitive data ingestion, oftentimes paying SIEM + DIY, increasing $ from complexity
- CTI team produces great reports, SOC consistently doing fire drills, >90% false positive rate, uneven distribution of skill (Tier 3)
4. Autonomic Security Operations Principles:
- ASO should
- Eliminate toil
- Embrace change
- Strive for continuous improvement
- Bridge all siloes
- Use service level objectives
- Avoid hero mentality
- Aim for simplicity
- ASO should not
- Restrict hiring to top professionals
- Require an engineering-only culture
- Increase overall tooling footprint
- Aim for incremental gain
5. Eliminate Toil : manual, repetitive, automatable, tactical, devoid of enduring value, and that scales linearly as a service grows
- Causes of Toil
- Too much technical debt
- Priorities or goals are not aligned
- Lack of training or support
- Lack of collaboration
- The business value to fix is too hard to realize
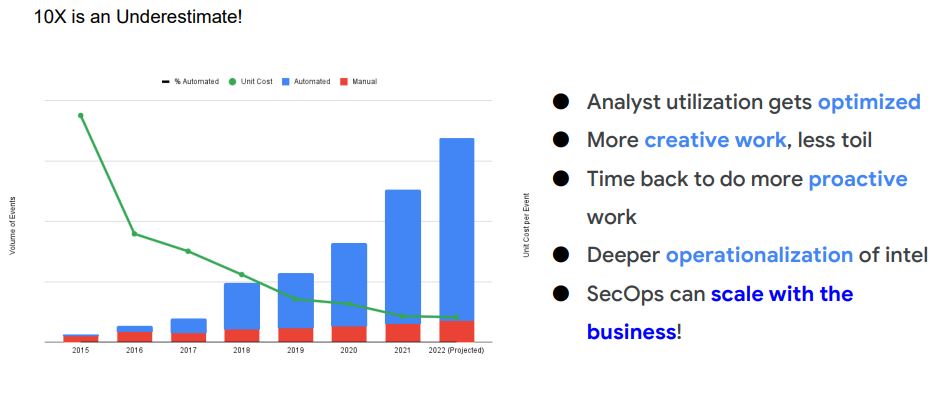
- Less Gathering, More Analysis – basics to automate
- Gathering machine information
- Gathering user information
- Process executions
- All context needed to help get to final (human) judgement
- Key Activities To Implement
- Train your team on toil & automation
- Create an Automation Queue
- Implement Blameless Postmortems
- Conduct Weekly Incident Reviews
- Implement SOAR
- Hire Automation Engineer(s)
- Implement CD/CR pipelines with metrics
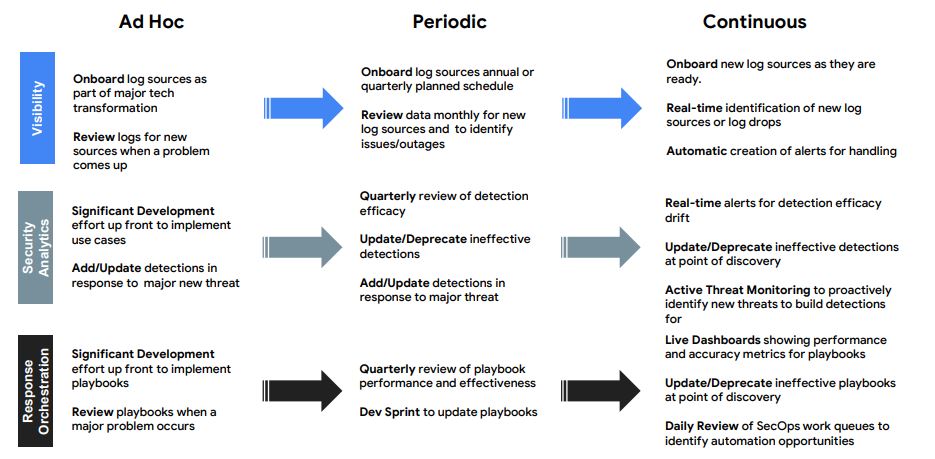
6. Evolve Automation
7. Practice Release Engineering
8. Strive for Simplicity
Complex systems require substantial human expertise in their operation and management. This expertise changes in character as technology changes but it also changes because of the need to replace experts who leave. In every case, training and refinement of skill and expertise is one part of the function of the system itself. At any moment, therefore, a given complex system will contain practitioners and trainees with varying degrees of expertise. Critical issues related to expertise arise from (1) the need to use scarce expertise as a resource for the most difficult or demanding production needs and (2) the need to develop expertise for future use.
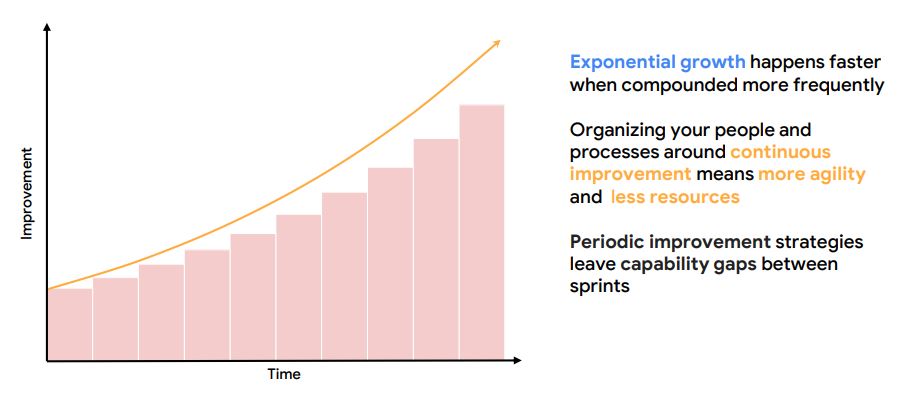
9. The Power of Continuous Improvement
10. Actions
- Reduce toil in your SOC - shift toil to machines
- Evolve automation in SIEM, SOAR, threat intel, etc
- Use SLOs / metrics to drive change
- Practice release engineering for consistent improvement
- Strive for simplicity with processes, technology stack, etc
We are hosting “Best Of The World In Security” Webinar On "DevOps Lesson For Your SOC (SRE)".
The 'Best Of The World' Series features the world's best security minds (researchers, inventors, subject experts, analysts). It covers security content and Q&A that is often hard to comprehend and you simply cannot ‘Google it’. This series has featured many great minds like Paul Raines (Nobel prize winner), Jacob Torrey (DARPA), Dr. Phil Polstra (Renowned Forensic Expert, BlackHat).
This is a community discussion with Dr. Anton Chuvakin (Ex Gartner Analyst, Security Advisor at office of the CISO, Google Cloud). We encourage you to make the most of it by inviting your teams and peer. You can send us your questions in advance or even ask live during the session in Q&A sections.
Why DevOps (SRE) ?
DevOps transformed IT and changed roles, practices and skills within IT. Security in general and security ops, in particular, are sometimes left behind. This session will share Google-inspired lessons of transforming detection and response practices using the approach we call Autonomic Security Operations.
Key Discussion Points :
- How does the security analyst role evolve?
- How security processes change in an ASO SOC?
- How automation reduces toil (and what is toil, anyway)
You can join us here: https://info.cisoplatform.com/sre/devops-lesson-for-your-soc?utm_src=CPblog
We had a community webinar on "Zero Trust : Architecture Principles; Threats; Architecture Components; Guidance Documents - NIST, CISA, NSA, DOD". We discussed history of the zero trust model, why is it relevant now ? (perimeter is dead, people work from anywhere and data is on endpoints and in the cloud), Zero trust architecture principles and tenets, Zero trust threats, Zero trust architecture components, Policy enforcement point types, Cloud deployment models, Zero trust guidance documents - NIST, CISA, NSA, DOD and more.
Session Agenda
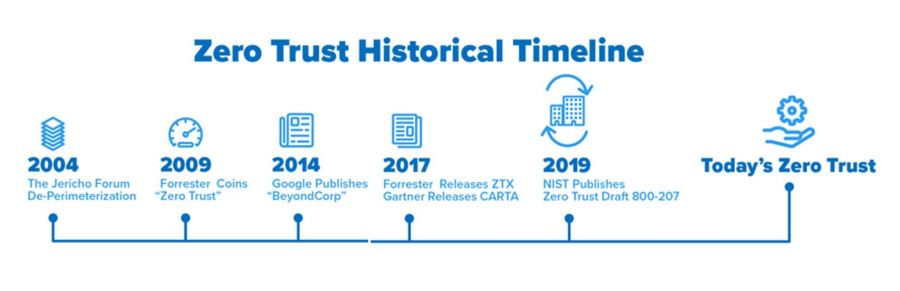
- History of the zero trust mode
- Why is it relevant now ? (perimeter is dead, people work from anywhere and data is on endpoints and in the cloud)
- Zero trust architecture principles and tenets
- Zero trust threats
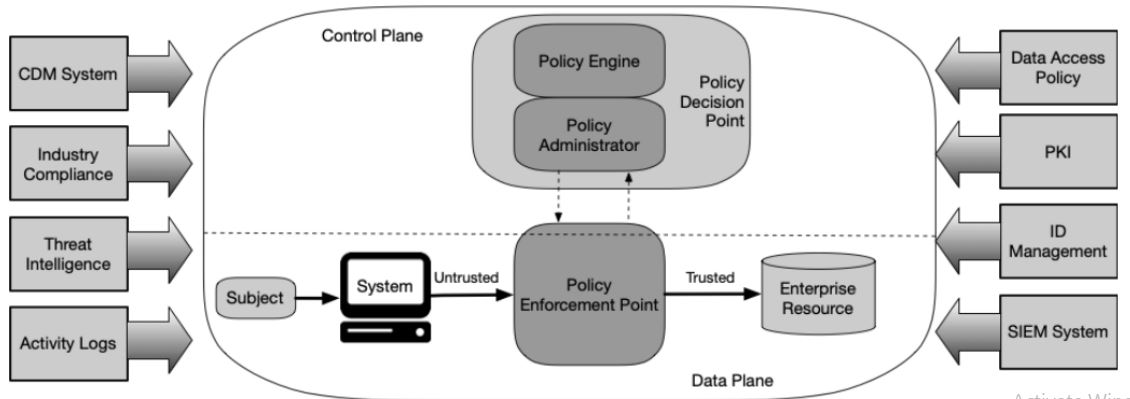
- Zero trust architecture components
- Policy enforcement point types
- Cloud deployment models
- Zero trust guidance documents - NIST, CISA, NSA, DOD
About Speaker
Wayne Tufek (Frequent Speaker RSAConference APJ, ISC 2, SACON & Renowned Security Architect) Wayne is currently on the board of the Melbourne Chapter of ISACA and holds the position of Vice President.
(Webinar) Recorded
Discussion Highlights
1. Why Zero Trust?
- Previous security models did not holistically apply important well known security principles
- Most Security architectures are like a cocunut
2. History of Zero Trust
3. Definition of Zero Trust
- Security model and set of design principles
- Threats exist both inside and outside traditional network boundaries
- Model Eliminates implicit trust in any one element
- Instead requires continuous verification
- Via real time information from multiple sources
- Model assumes that a breach is inevitable or has likely already occurred
- Limits access to what is needed and looks for anomalous or malicious activity
- Embeds comprehensive security monitoring; granular risk based access controls
- Data centric model allows the concept of least privilege to be applied for every access decision
4. Tenets
- Identity & Inventory is key - know your users, devices, services and data
- Trust is not based on device's network location - the network is always assumed to be hostile
- Every device, User and network flow is authenticated and authorised
- Access is based on context, for example the identity of the user, the device being used etc
- Devices may be company owned or owned by the User
- Access is granted on a per session basis
- All communication is secure
- Access to resources is determined by dynamic policy and observable state
- Strong authentication is used
- Continuous logging, monitoring and posture assessment
- Monitoring should be an ongoing basis to access risk, access is adaptive and varies based on context
- Assume breach - an attacker is already on our network
- External and Internal threats exist at all times
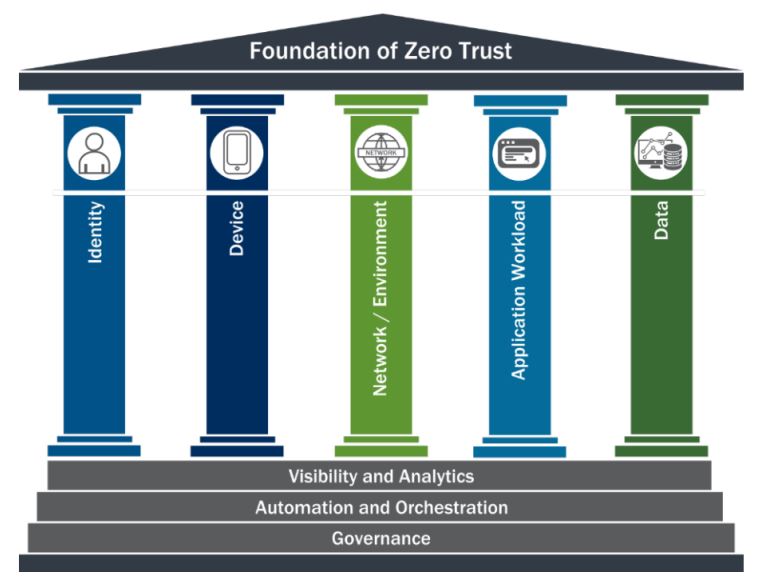
5. Foundation Of Zero Trust
6. Logical Components
7. Benefits
- Support work from anywhere
- Prevention First
- Protect resources regardless of their location
- Better address threats
- Limit an attacker's ability to move laterally
- Users connect directly to services and not to the network
- Improve incident detection and response
- Improve visibility
- Dynamic risk-based assessments = better defence
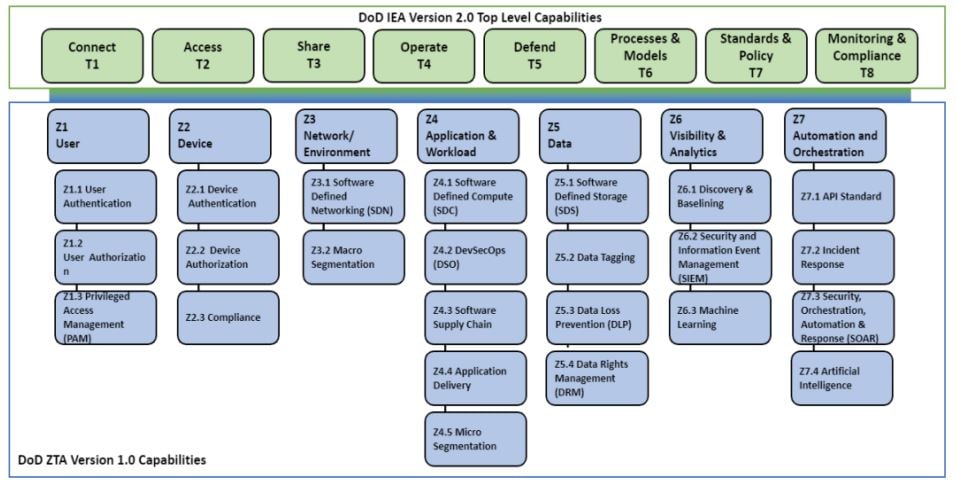
8. Capabilities and Services
9. Implementing Zero Trust
- Users
- Centralised enterprise managed identities
- MFA (application layer enforcement, Phishing resistant, passwords)
- Check password against known breaches
- At least one device level signal during authentication
- PAM
- ABAC
- RBAC
- Devices
- Maintain a complete reliable inventory of assets
- EDR
- Networks
- Network visibility
- Encrypt DNS requests
- Use HTTPS for web application and APIs
- Plan for Network isolation
- Applications and Workloads
- Understand your network protect surface
- Treat all applications as internet connected
- Have a dedicated application security testing program
- Operate an effective and welcoming public vulnerability disclosure program
- Work towards employing immutable workloads
- Data
- Categorise and tag your assests
- Audit access to any data encrypted at rest in a commercial cloud
- Implement comprehensive logging
- Automate security responses
- Key Steps
- Decide to adopt a zero trust strategy
- Inventory your environment
- Determine your current state
- Set desired maturity
- Don't forget governance
- Start with identity and device security
- Slow and steady - work with your existing capabilities first
- Ditch passwords
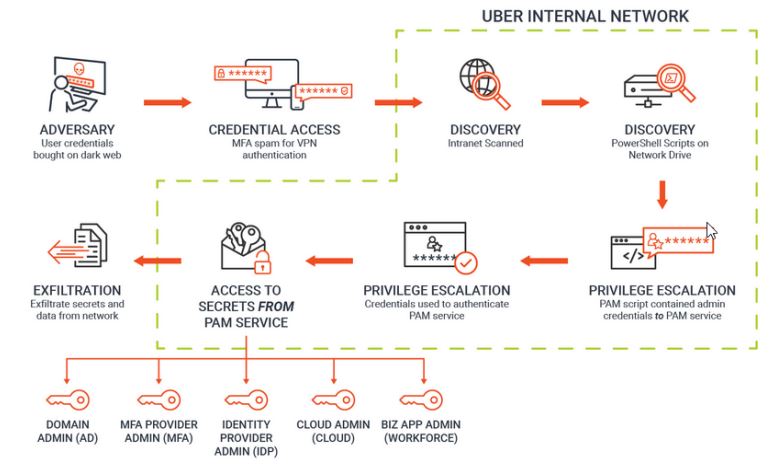
10. Zero Trust In Action : Deconstructing the Uber Attack - what we reportedly know
We had a community webinar on "XDR : A Holistic View Through Security Analytics – Across Endpoint, Network And Cloud". We discussed the fundamentals; Endpoint solutions vs XDR; Implementation experience, challenges; post implementation feedback, outcome vs expectation, use cases; MDR vs human skills.
Session Agenda
- What is EDR, XDR
- Endpoint solutions vs XDR
- Implementation experience , challenges
- Post implementation feedback, outcome vs expectation, use cases
- MDR vs human skills
About Speaker
- Abdur Rafi, Head IT Infrastructure & CISO, ABP Group
- Soumya Biswas, IT Infrastructure & Security Specialist, ABP Group
- Debajyoti Das, Senior Executive IT Security, ABP Group
(Webinar) Recorded
Discussion Highlights
1. Extended Detection and Response (XDR) solutions are designed to provide automated threat detection and response through data visibility and the use of threat intelligence and data analytics. XDR collects activity data from multiple vectors including endpoints, servers, and networks.
2. Automobile Attack Surfaces : Fifteen of the most hacable and exposed attack surfaces, including several electronic control units on a next generation car. Like - Smartphone, Remote link type app, Airbag ECU, OBD2, USB, Bluetooth, DSRC-Based Receiver (V2X), Remote key, Passive keyless entry, Vehicle access system ECU, Steering and Braking ECU, Engine and Transmission ECU, Lighting system ECU, ADAS system, TPMS
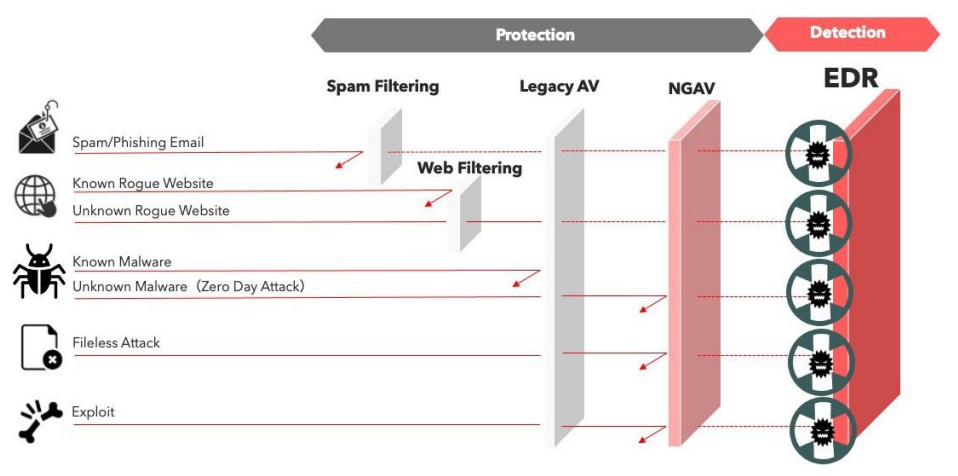
3. Endpoint Detection & Response
- Spam Phishing email
- Known Rogue eebsite
- Unknown Rogue website
- Known Malware
- Unknown Malware
- Fileless Attack
- Exploit
4. Endpoint Protection Plan (EPP)
Detection : Ioc scan, Advanced detection techniques, Behaviour analysis
Investigation : Root cause, Attack Visualization, Enriched alert data
Response : Automated response on discovery, Multiple response options, Quick response during the investigation
5. How XDR works : XDR isolates and dissects threats on different attack surfaces
- Endpoints
- Network
- Servers
- Cloud workloads
6. Endpoint Protection Policies
- Threat Protection
- Peripheral control
- Application control
- Data Loss Prevention
- Web Control
- Update Management
- Windows Firewall
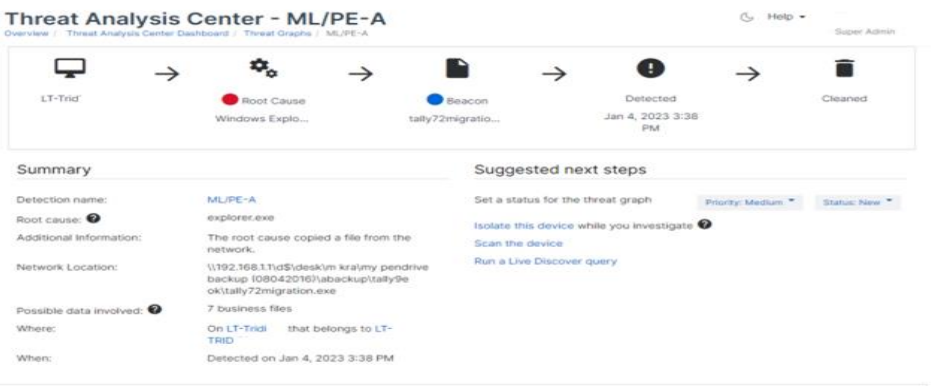
7. Threat Analysis Center - ML / PE-A
We are hosting CISO Community Webinar on "Zero Trust : Architecture Principles; Threats; Architecture Components; Guidance Documents - NIST, CISA, NSA, DOD"
Join us for "CISO Webinar : Zero Trust From A Practitioner's Perspective (Architecture Principles; Threats; Architecture Components; Guidance Documents - NIST, CISA, NSA, DOD)" with Wayne Tufek (Frequent Speaker at RSA APJ, ISC2, SACON & Renowned Security Architect). In current enterprises, data and resources are distributed across multiple clouds and premises with users needing access anytime anywhere. Thus, data protection needs to be beyond the enterprise environment perimeter. A zero-trust architecture (ZTA) enables secure authorised access to each individual resource, whether located on-premises or in the cloud, for a hybrid workforce and partners based on an organization’s defined access policy. The challenge for security professionals investigating a Zero Trust strategy is looking beyond the buzzwords of vendors and the hype.
Key Learning Points :
- History of the zero trust mode
- Why is it relevant now ? (perimeter is dead, people work from anywhere and data is on endpoints and in the cloud)
- Zero trust architecture principles and tenets
- Zero trust threats
- Zero trust architecture components
- Policy enforcement point types
- Cloud deployment models
- Zero trust guidance documents - NIST, CISA, NSA, DOD
You can join us here: https://info.cisoplatform.com/zero-trust-architecture-principles-threats-architecture-components-guidance-documents-nist-cisa-nsa-dod
We had a CISO community Fireside on "Practical Approach To Understanding Attack Surface Management (ASM) In 2023" with Chris Ray (security architect) and Bikash Barai (cofounder CISO Platform, FireCompass). We discussed on how ASM dramatically improves visibility, how ASM can be a force multiplier for security teams that are stretched thin, case studies, ASM solution market and how to evaluate a 'Good Fit for your organization'.
Key Points
- How ASM Improves Visibility And Creates Practical Risk Reduction?
- ASM Case Studies
- ASM Solution Market And How To Identify A Good Fit For Your Organization?
About Speaker
- Bikash Barai, Co-Founder, CISO Platform & FireCompass
- Chris Ray, Security Architect
FireSide Chat (Recorded Version)
Executive Summary (FireSide Chat Highlights) :
1. What Is Attack Surface Management (ASM) ?
ASM is just too concise it's too accurate it's it's very descriptive. When we are talking about attack surface management, it's really important to understand if you have never considered it, you have never looked under the covers. It's really important to understand, it is a paradigm shift away from a lot of security practices and tooling. I'll give examples from EDR to help illustrate this. You need to know end point to install the agent on it and take advantage of the EDR solution. For vulnerability management, one must know their repositories to be able to scan and protect them. ASM takes away the shortcomings of legacy vulnerability scanning platforms that are network based. Legacy vulnerability scanners continuosly scan available assets, however this approach could fail if the assets being scanned is not the universe of assets of the company. That's a major problem for a lot of organizations. ASM takes a different approach, it scours the internet, uses automation and human expertise to look for breadcrumbs of data and information based off from One initial starting point like a company domain. With this, ASM build a very comprehensive understanding of an organization's digital footprint.
Sometimes ASM is split as External Attack Surface Management (EASM) and Internal Attack Surface Management. EASM is the publicly exposed data which attacker's could easily misuse. However, this differentiation is not so crucial, I won't care if it's internal or external, I would care about the priority based on high-risk low-risk vulnerabilities.
2. What is the reason behind the rise of ASM ?
It is wise to note majority of attacks that take place are at a much lower sophistication level. Shodan is the search engine for IoT, Shodan it's like Google but for Internet connected stuff. Attacker focused enablers of technology have now existed for a while and that puts a lot of data in the hands of attackers which could get misused. I see this as a catalyst for products like ASM. The next I think that drives a solution like ASM are small teams at startups. A good ASM not only enables the security team with an organization's attack surface but also helps with understanding comtext and provide a method of prioritizing where to start. This is a pretty hard problem ASM solves the prioritization. ASM also comes in handy since it immediately notifies when a new patch is released.
3. What Are The Key Pain Points And The Use Cases Of ASM ?
There are 2 main segments here the large enterprises with merger and acquisition activity, ASM helps with a scan of all resources which is a very time consuming and expensive activity otherwise. Another use case is for large enterprise and government where they are consolidating their business units, a unified list of assets for each unit is a quick view very meaningful to them. Discovering the assets becomes a beginning point for defining their cyber security framework.
Another place of use for ASM comes in smaller organizations or SMB or startups with overworked small security teams. An ASM which prioritizes the vulnerabilty and what to work on, makes sure you are putting the right fire out. The smaller teams don't have the bandwitdth to figure this out, there are way too any things to attend to already.
Another place of ASM value comes in for all security teams, vendor risk management tools might throw vulnerabilities not deduplicated while the ASM could add a very comprehensive report in this case. It save the security team from spending hours on vendor risk management.
ASM adds a huge amount of insight for the security architects. They build the framework and have a deep understanding. The ASM report is of great help to them vs the engineers and analyst who often have a top level view.
ASM reports are extremely useful for security teams like the GRC team, vulnerability management team, security leadership, cloud security posture management teams. There's interesting augmentation amongst SOC and ASM; Threat Intelligence and ASM, it just gives them more data to work on and adds value on it.
4. How ASM Helps In The Risk Management Story ?
Many organizations and security leaders have become comfortable with making risk management decisions in a vacuum. An ASM bridges that gap and empowers a leader with the assets and repository information to help protect their organization. It is adding the context for risk management decision making. That doesn't need to be manual or ad hoc, ASM is doing it in a structured way. With the ASM reports, the security leader (or leadership team) has comprehensive asset data and context with each, so now he/she no longer is making decision in the vacuum but with context and priority. The ASM tool basically starts with base information like IP DNS hostname and it builds on it like the AWS asset or unbuntu server with context on the asset. It could add context like the DNS records changed on this date and previously it was owned by this organization and in this geography, later start stringing together additional context. So now, the person no longer had to make decisions in a vacuum, he/ she has a more comprehensive understanding of where this asset fits into the bigger picture of the organization.
5. From Where Do Organizations Get The Budget ?
Is it like they're taking some existing budget or creating a new budget and also like how are they justifying the budget ?
There are two primary ways that this is getting purchased. Shifting away from their vulnerability management. The best way to think about this is ASM is doing what you should already be doing but you can't. Organizations did not have the full view of all the assets once they got to know all those assets these are like half of it we don't need it they shouldn't be online.
I see there are 2 primary ways this is being purchased - one is creating budget by shifting away from the vulnerability management (not entirely since there are a few must like the compliance frameworks, regulatory frameworks, network-based vunerability scans) by primarily using ASM and then complimenting it with the compliance, regulatory, network based scans. So now you need not spend as much money on the remaining vulnerability management (compliance, regulatory, vulnerability scans). So cutting out a part of this for ASM and cobbling these with ASM.
Another area for ASM budget is asking for new money. It is always hard to get new money and really needs good justification. For ASM one major justification for a security leader is it allows him/her to get a comprehensive view of their asset repository which is a primer for being able to secure in the first place. Most security leaders agree they need to do this but donot have the resource (army of engineers and skill and continuos monitoring) to do it. An ASM is that tool that gives you value out of the box. Not many security teams will have the resource to hire the army of engineers and map out their attack surface thought they know it's a necessity. It is also a lot more expensive while an ASM tool is doing just that for much less.
It is interesting, we noticed in the past some organizations (even large Fortune 500), found out plenty of online resources they were still paying for and weren't using. With ASM, they found it and took it off, saving them cloud costs (turned out it was a big annual expense save).It was an asset marketing created and had collected customer data on it. Nobody was maintaining it anymore. So it was laying out there anyone could have exploited it. With GDPR, it would have then costed them a huge amount for this too. So, in ways ASM actually helped them reduce their attack surface and saved them money by preventing a data breach and saving cloud costs.
6. What Are The Challenges In ASM As A Space ?
It is a hot space but not in its super mature stage
Firstly, ASM maps your attack surface which is like 95% but there will be some parts more to it. ASM is improving with time and evolving. So a mistake easy to make is ASM is giving me the full picture. There may still be a few areas undiscovered, it's nor perfect and it's important to be ready for that 5%. It's the low hanging fruits that get jabbed first and cause the breach mostly. One has to remember ASM is still a tool made by humans to help you make secuity decision but it will have its flaws. ASM as a technology is excellent at discovering and it's almost perfect, but one must be vary of the little part that still stays uncovered (no tool is perfect). Despite the best efforts, computer science is very effective but not perfect, so there will be misses even from the ASM tool, be vary of it.
ASM is really good at the external attack surface mapping and there seems to be a direction where some vendors and ASM solutions are building similar capabilities (not exactly same) for the internal attack surface too. Whether on premise or on cloud, one must not leave out this area of 'internal attack surface' as this still can be a major threat area. Your organization attack surface includes the external attack surface (EASM) and the internal attack surface for a holistic view, even if multiple tools do it.
ASM faces a challenge as to many false positives and prioritizing this. Legacy vulnerability management shows you what's broken while ASM finds more assets more broadly and is more comprehensive but their functionalities are separate. ASM is trying to handle the problem of false positives by adding context, it comes back with the vulnerability and proof like screenshots or commands and potential damage. ASM Tools are trying to automate this and also adding humans in the loop at the last mile for validation. Another way to solve this could be by ASM becoming a part of security suite rather than being a standalone tool. It could become a part of cloud security or SOC or vulnerability management. Essentially ASM will evolve and possibly become a part of the security suite.
We are hosting CISO Community Fireside chat on "Practical Approach To Understanding Attack Surface Management (ASM) In 2023".
Join Chris Ray (Analyst, Gigaom, Domain expert Attack Surface Management), Bikash Barai (Co-founder, Cisoplatform , CEO, Firecompass). We will understand how ASM dramatically improves visibility, how ASM can be a force multiplier for security teams that are stretched thin and how ASM creates practical risk reductions because of these (visibility and force multiplier). We will also understand the ASM solution market and 'How To Identify A Good Fit For Your Organization.
Key Learning Points :
- Fundamentals : What Is ASM? How Does ASM Work ?
- How ASM Dramatically Improves Visibility ?
- How ASM Can Be A Force Multiplier For Security Teams ?
- How ASM Creates Practical Risk Reduction ?
- Understanding ASM Solution Market
- How To Identify A Good Fit For Your Organization ?
You can join us here: https://info.cisoplatform.com/practical-approach-to-understanding-attack-surface-management-asm-in-2023
We had a CISO community webinar on "Exposure Management For Financial Institutions To Overcome Resource Limitations And Regulatory Reporting". We discussed how to overcome resource limitations and the manual burden of regulatory reporting. How exposure management can help your Institution navigate the ever-increasing regulatory burden.
Session Agenda
- How to Overcome Resource Limitations: automate and lighten your workload by providing continuous programmatic assurance
- Discover, Prioritize & Proactively Reduce Cyber Risk: Discover your attack surface risks & prioritize the most important ones to help mitigate the risks faster
- Security Posture Reports to Meet Regulatory Requirements: How to continually assess and provide automated reports on your security posture to meet regulatory requirements
About Speaker
- Bikash Barai, Co-Founder & CEO, CISO Platform & FireCompass
- Dave Lawy, Co-founder QunatumSmart and Senior Technology Executive
- Nasheen Liu, Partner & SVP, CIO Program Strategy
(Webinar) Recorded
Discussion Highlights
1. In both USA & Canada the regulators are stepping up the level of sophistication demanding higher level of cyber security maturity from Financial Institutions. Any comments ?
- What are some of the ways Financial Institutions provide continuous assurance of their cyber posture?
Context: Good process is always important however automation is the key to being successful in any space.. automated cyber tooling will help setup the company for success - What is a general trend of interactions observed by regulators with industry on cyber?
Context: Better processes, Less tolerance for poor hygiene, better questions & maturity matrix
2. Is Cyber Insurance important and how does it best serve the organization ?
- The price of insurance is significantly increasing YearOnYear, retention (deductible) is increasing while exclusions and / or endorsements are reducing risk for the insurance carrier. Mitigating controls are more and more necessary
3. How can FI (Financial Institutions) best demonstrate they are adhering to security standards and compliance frameworks such as PCI DSS or SOC 2 and how are these standards maintained and updated ?
- Standards require regular maintenance, adhering to a process and providing evidence. The more that can be automated the better the evidence is to showcase the organization adheres to such standards, better consistency, repeatable, predictable output
- As the environments increase complexity so does the ability to adhere to increasingly more stringent standards and frameworks. It is important to have systems and applications designed, built, and delivered leveraging automation. DevSecOps is a somewhat newer term however this has been around for some time in different forms. Ultimately security has to be built into the design. The systems state must be controlled programmatically which would allow proactive and reactive security changes to be made efficiently and in a scalable manner
4. What is External Attack Surface Management (EASM) and why is it Important ?
- Failure to conduct an extensive attacker-like reconnaissance frequently leaves low-hanging fruits easily exploited by cybercriminals. And because attack surfaces are dynamic you will want continuous attack surface mapping and security testing especially on assets residing in “Shadow IT” for your organization and third parties
5. What are some of the trends being seen regarding cyber people resources and how are companies coping with the ever increasing demand on cyber resources as the threat landscape increases ?
- War on talent, shortage of staff, constraints on budget, increasing demand to protect / defend, more sophisticated attack vectors…shortage of CISO thought leadership
6. Financial Institutions must adhere to standards and practices. How can the Financial Institutions perform expensive security exercises to protect and defend with a security team that has a long list of priorities, along with a shortage on staff and time
- FireCompass CART - Our CART platform gives you multi-stage attack playbooks to mimic a real attacker and accurately pinpoint prioritized vulnerabilities that would be targeted first. CART delivers shorter mean time to remediation (MTTR) and increased depth and breadth of coverage so you can focus on your mission of keeping attackers out and keeping IT/OT services running smoothly and securely.
Gartner says “Nation-state actors and criminal organizations operate with a level of sophistication that surpasses the preventative and detection capabilities of most security and risk management teams.”
7. How about leveraging SaaS security solutions and automation to augment the security team
- Having such tooling with repeatable predictable output and evidence of processes not only helps with regulators but this can be a powerful tool for Third Party Risk Management. If your customer or vendor is using automation, there is a clear audit trail a known process in place that is standardize…this helps in audits as both a customer and vendor…. Third-party risk management: Financial institutions must ensure that third-party vendors and partners who have access to their systems and data are appropriately vetted and managed for cybersecurity risks.
8. What is Cyber risk and how can today’s FI best manage risk
- FireCompass is a SaaS platform for Continuous Automated Red Teaming (CART) and External Attack Surface Management (EASM) that acts as an integral part of a good exposure management program.
-Single Platform for Attack Surface Management and Automated Penetration Testing & Red Team
-Daily Risk Port Scanning & Adversary Emulation through multiple Attack Playbooks
-Prioritized Risks with real-time alerts for faster detection and remediation
- Understand your holistic technology landscape. Understand all your assets logical, physical. Understand your level of maturity measured against regulatory standards, understand your exposures, Understand your processes to mitigate, Understand your tooling and systems to mitigate and understand your organization and culture.
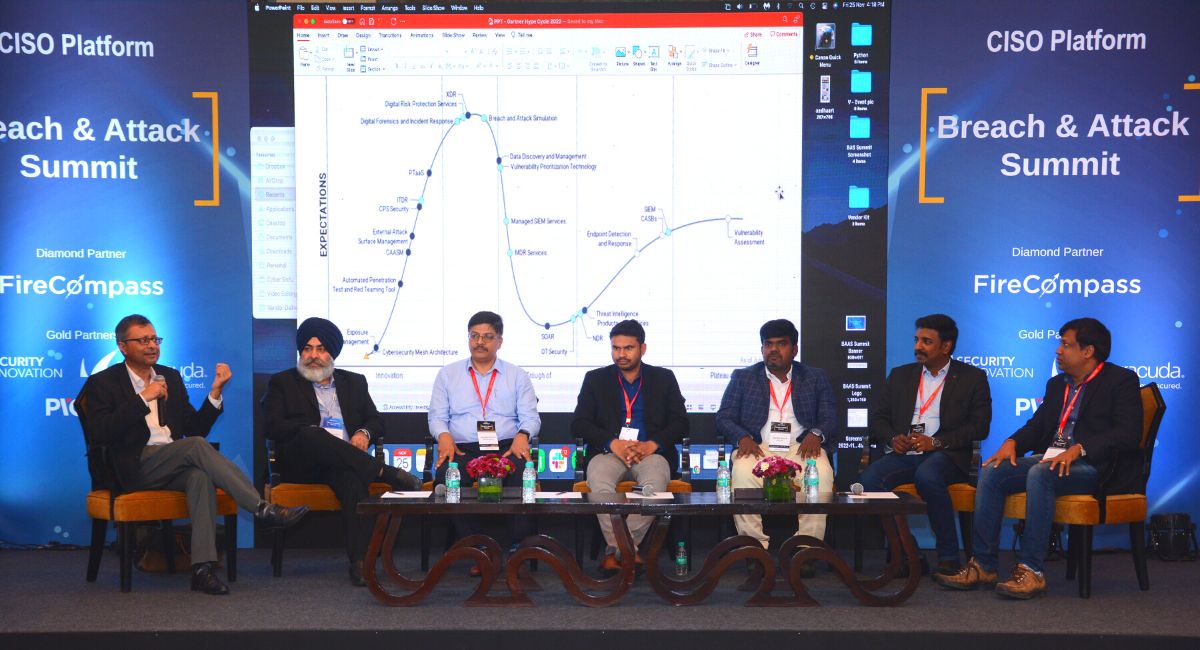
We did 3 panel discussions in 3 cities, engaging over 25+ CISOs on the Gartner Hype Cycle for Security Operations that is used by CISOs to identify the hype and expectations and insight into what technologies and trends are likely to become more important in the near future.
Panel Speakers
- Somshubhro Pal Choudhury, Partner, Bharat Innovation Fund
- R Nantha Ram, Leader - Cyber Security Operation, 3M TCOE
- Naseem Halder, CISO, ACKO General Insurance Ltd
- Nitish Goyal, Director, Ocwen Financial Services
- Philip Varughese, Global Head - Applied Intelligence, Platforms and Engineering, DXC Security
- Sandeep Bansal, Head ICT, Reva University
- Harmeet Kalra, Regional Sales Director (India & SAARC), Picus
Discussion Highlights
1. From the Gartner Hype Cycle- Pick 1-2 areas you are personally excited about… what you think is the need of the hour
Here are the top emerging technologies picked by CISOs:
- External Attack Surface Management
- Exposure Management
- Automated Penetration Test & Red Teaming
- PTaaS
- Digital Risk Protection Services
- XDR
2. What's your focus on the new entrants and its importance in the near future
As Gartner recommends, “Expand to a broader exposure management to include unpatchable attack surfaces and assess the need for solutions, such as digital risk protection services (DRPS), external attack surface management (EASM) and/or security rating services (SRS) for coverage of other exposure points, such as supply chain and shadow IT in the cloud”.
- Scalability: The technology should be able to scale to meet the organization's future needs
- Continuous monitoring: CISOs should continuously monitor the technology for any issues or vulnerabilities and have a plan for incident response
- Compliance & Governance: The technology should comply with any relevant regulations and industry standards. CISOs should ensure that the new technology aligns with the organization's overall governance and compliance policies
- Automation: products can be leveraged to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of security processes, and can free up resources to focus on more strategic initiatives. Automation can also help to reduce the risk of human error and improve the speed of incident response
- Integration: The technology should be able to integrate with existing systems and processes within the organization
- Risk Management: CISOs should assess the risks associated with the adoption of new technology, and have a plan in place to manage those risks
- Staffing: Adequate staff and resources should be in place to support the new technology, including training and support for end-users
- Business Impact: The new technology should align with the organization's business goals and objectives
- Continuous improvement: CISOs should view the adoption of disruptive technologies as an opportunity to continuously improve and adapt the organization's security posture, and not as a one-time event
Join Bikash Barai (co-founder CISOPlatform Community & FireCompass) and Dave Lawy (Co-founder QunatumSmart and Senior Technology Executive), as they discuss how to overcome resource limitations and the manual burden of regulatory reporting for Financial Institutions.
- How to Overcome Resource Limitations: automate and lighten your workload by providing continuous programmatic assurance
- Discover, Prioritize & Proactively Reduce Cyber Risk: Discover your attack surface risks & prioritize the most important ones to help mitigate the risks faster
- Security Posture Reports to Meet Regulatory Requirements: How to continually assess and provide automated reports on your security posture to meet regulatory requirements
Phishing is the fraudulent practice of sending emails or other messages purporting to be from reputable companies in order to induce individuals to reveal personal information, such as passwords and credit card numbers. This article highlights some major phishing types as a guide for reference.
Phishing scams are a type of social engineering attack that use fake emails or websites to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords, credit card numbers, and social security numbers. These scams often appear to come from legitimate organizations, such as banks or online retailers, and may contain urgent requests for personal information or threats to close accounts if information is not provided. To avoid falling victim to a phishing scam, it's important to never click on links in suspicious emails, verify the sender's email address, and never enter personal information on a website unless you are certain it is legitimate.
From a recent report, SlashNext's State of Phishing report reveals that there were 255 million phishing attacks in 2022, a 61% rise from the previous year. The attacks are getting more sophisticated. Recent examples show phishing emails are able to bypass Gmail's filter. The examples below might help prevent yourself from a few common phishing attacks patterns by raising awareness.
P.S. I have taken excerpts from various interesting blogs online mentioned in the reference section
The types of phishing include :
- Spear Phishing : Spear phishing involves targeting a specific group or individual, such as a company's system administrator. The following is an example of a spear phishing email. Observe the focus on the recipient's industry, the requested download link, and the urgent nature of the request.
- Whaling : Whaling is a highly targeted form of phishing that targets "the whales" - high-level executives within an industry or business, such as a CEO, CFO, or CXX. These attacks often claim that the company is facing legal trouble and require the recipient to click a link for further information.
- Vishing : Is similar in nature to other phishing attacks, with the goal of obtaining sensitive personal or corporate information. This type of attack is carried out through voice calls, hence the "v" in the name instead of "ph".
- Smishing : It is a type of attack that uses text messaging or SMS to deceive the target. A typical smishing tactic involves sending a message to a cell phone through SMS that contains a clickable link or return number.
- Email Phishing : The most prevalent form of phishing, has been in use since the 1990s. Attackers send these emails to any email addresses they can obtain, often claiming that there has been a breach to your account and requesting immediate action through a provided link. These attacks are often easy to identify due to spelling and grammar errors in the email. However, some phishing emails are harder to detect, especially when the language and grammar are polished. Checking the email's source and the linked website for suspicious language can provide clues as to its legitimacy
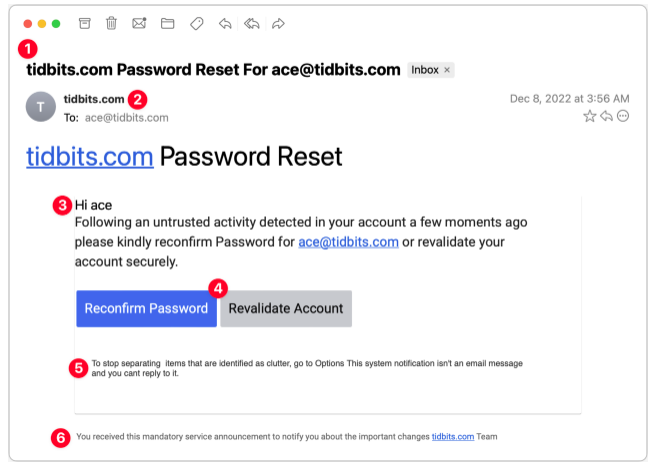
A.Password Reset
This phishing scam appears to originate from a system administrator responsible for my email domain and attempts to entice me into clicking a button. Although the text is poorly written, the buttons are well-designed, making it easy to imagine someone clicking without fully reading the text, especially if they are scanning quickly.
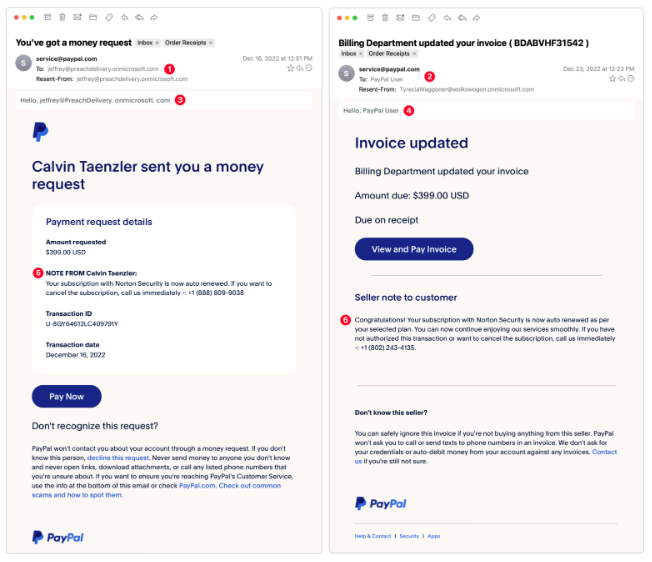
B.PayPal Money Request
These are exceptionally clever as they utilize authentic PayPal messages and include multiple anti-phishing warnings in the text. Despite this, there are still signs that give away their true nature. These messages arrived a week apart and are likely the result of a single phisher.
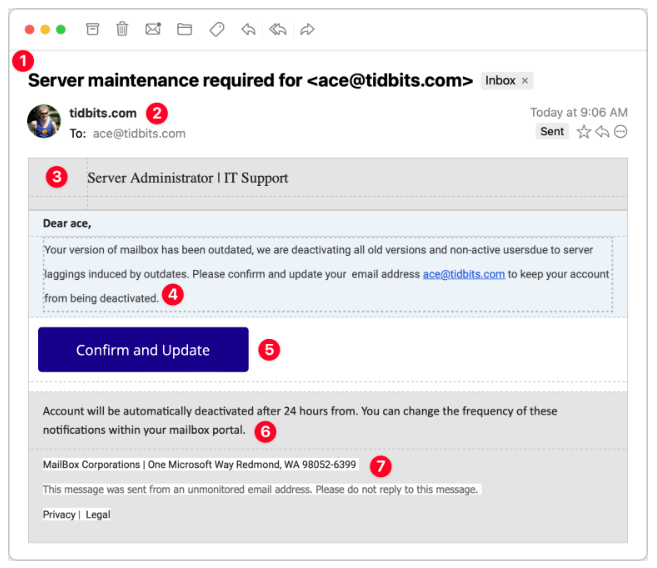
C.Server Maintenance
Consider this message claiming to be from my company's IT Support team. Its goal is to obtain your email password, as once an attacker gains control of your email, they can reset passwords on other sites and access sensitive accounts. It is crucial to safeguard your email password the most!
Some common patterns to be aloof of :
- Give emails a full read. Do not click if you have only skimmed through it. Be careful with easy emails and big buttons. Read the text carefully firsy before clicking. Look for grammatical errors, spelling mistakes in the email
- Verify with your IT department in person before honouring the claim on email
- An email with only an attached image and nothing else is mostly problem
- Be vary of the sender name and email addresses. Check for known ones.
An interesting question..can you mention the tell away signs in each phishing email example ? Comment below
Reference
- https://tidbits.com/2023/01/16/an-annotated-field-guide-to-identifying-phish/
- https://www.schneier.com/blog/archives/2023/01/a-guide-to-phishing-attacks.html
- https://cybersecurityguide.org/resources/phishing/
- https://www.valimail.com/guide-to-phishing/#:~:text=Most%20phishing%20attacks%20arrive%20via,tricking%20users%20into%20downloading%20malware.
- https://www.trendmicro.com/en_us/what-is/phishing/types-of-phishing.html
.png?profile=RESIZE_710x)












/Banner%20with%20partner%20logo.png)
/Speakers.png)